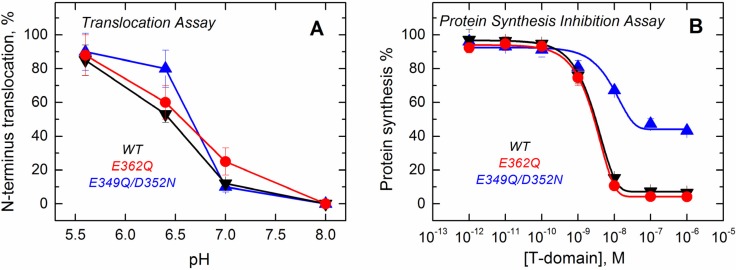
Figure 9.
Functional assays to study the activity of the T domain WT (black) and the mutants E362Q (red) and E349Q/D352N (blue). (A) The translocation activity of the isolated T domain, carried out by using a proteolytic assay that cleaves the N-terminus when translocated to the lumen of thrombin-loaded vesicles, indicates that both of the mutants have a level of activity similar to that of the WT; (B) The cell death assay with the entire toxin, performed using the protein synthesis inhibition assay by measuring the [3H]-leucine incorporation in treated cells and normalized against untreated cells, shows that only the double mutant E349Q/D352N loses part of its activity. Each point is the average of four replicates. Error bars correspond to the standard deviation.