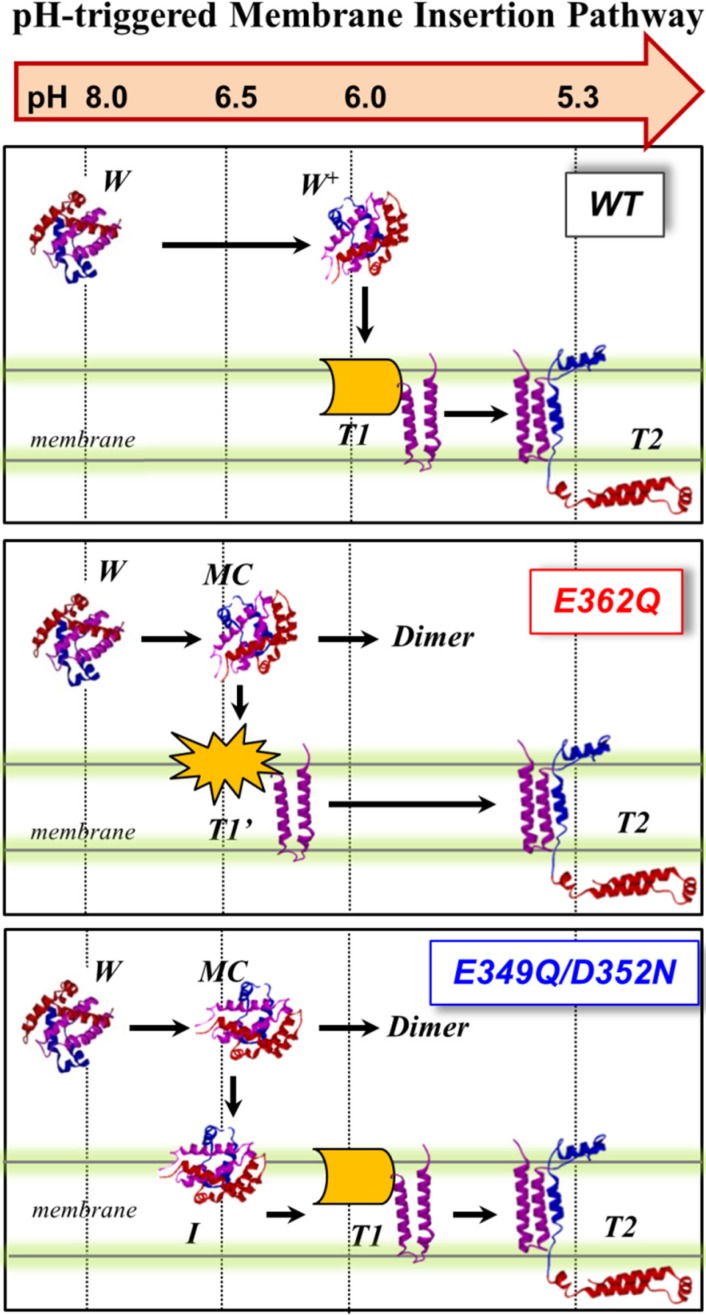
Figure 10.
pH-dependent membrane insertion pathway of the T domain WT and the mutants E362Q and E49Q/D352N. For the WT, the pathway consists of an initial conformational change in solution (membrane-incompetent W-state to membrane-competent W+-state), followed by association with the membrane and transbilayer insertion into the T-states. The T1- and T2- states are states with the N-terminus located on the cis and trans side of the bilayer, respectively. For both mutants, the formation of a membrane-competent state (MC-state) is shifted towards less acidic conditions. Without a membrane, aggregation occurs under less acidic conditions than the WT. With a membrane, E362Q readily inserts into the bilayer, while the double mutant accumulates interfacially (I-state). The N-terminal region of E362Q misfolds within the membrane interface; nevertheless, additional acidification results in the completion of the pathway and formation of the functional inserted state.