Figure 3. Photoinhibition of CeM projectors impairs fear learning and enhances reward learning.
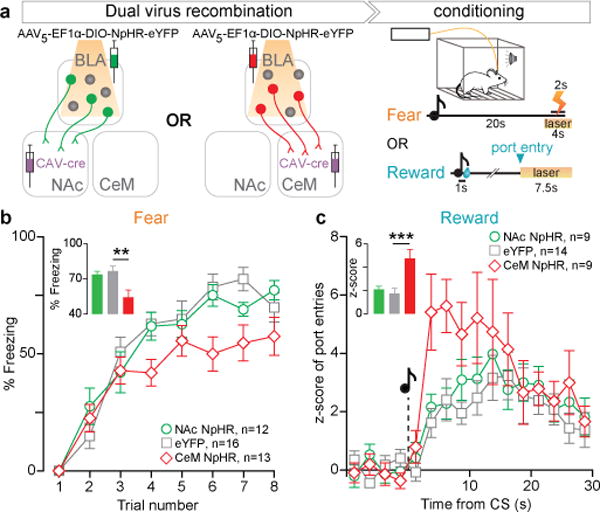
a, Halorhodopsin (NpHR) was expressed bilaterally either in NAc or CeM projecting BLA neurons using a dual-virus recombination strategy. Mice underwent fear or reward conditioning, and yellow light was delivered to the BLA during the US. b, Time course of percentage freezing and average freezing in trials 6–8 (inset). Average freezing was related to experimental condition (one-way ANOVA, F2,40=6.68, **P=0.0033) and was significantly reduced by photoinhibition of CeM projectors, relative to controls (t38=3.46, **P<0.01; see inset). c, Time course of normalized number of port entries, relative to cue presentation during reward conditioning and average number of normalized port entries (< 8 s latency, inset). Z-score of port entries was related to the experimental condition (one-way ANOVA, F2,31=9.23, ***P=0.0008) and was significantly increased by photoinhibition of CeM projectors, relative to controls (t29=4.11, ***P<0.001). Results show mean and s.e.m.
