Extended Data Figure 3. Paired Pulse Ratio and AMPAR/NMDAR ratio in non-learners and food restricted naïve animals.
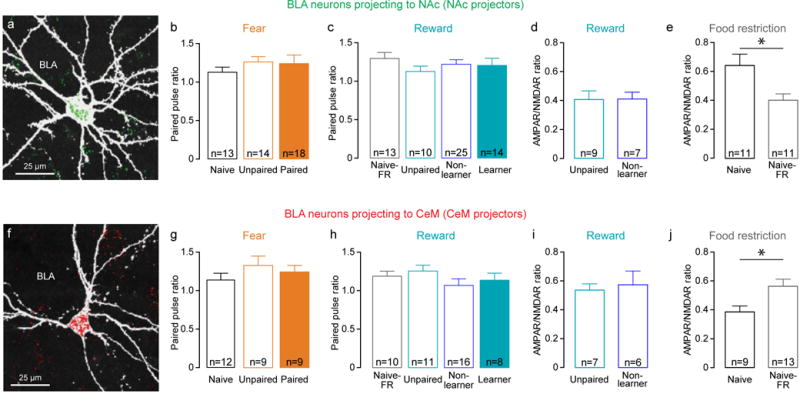
a, Confocal image of a representative retrobead positive neuron recorded in BLA after injection of retrobeads into NAc. This cell was recorded in an ex vivo slice, filled with biocytin and stained with streptavidin-CF405, pseudocolored white. b, In NAc projectors, the ratio of EPSC amplitude in response to paired-pulse stimulation (50 ms inter-pulse interval) of internal capsule inputs to the BLA was not related to experimental conditions of fear (one-way ANOVA, F2,44=0.5209, P=0.5978). c, Paired-pulse ratio of EPSC amplitude was not related to experimental condition of reward (one-way ANOVA, F3,61=0.5868, P=0.6261). d, AMPAR/NMDAR ratio of internal capsule inputs onto NAc projectors in mice with unpaired tone and sucrose presentations (Unpaired) and mice that did not learn the cue-reward association (Non-learner). Both groups of mice received the same amount of total sucrose. e, AMPAR/NMDAR ratio onto NAc projectors is significantly decreased by food restriction in naïve mice (unpaired t-test, t20=2.626, *P=0.0162). f, Confocal image of a representative retrobead positive neuron recorded in BLA after retrobead injection in CeM. g, Paired-pulse ratio of EPSC amplitude onto CeM projectors is not related to experimental conditions of fear (one-way ANOVA, F2,29=0.9040, P=0.4169). h, Paired-pulse ratio of EPSC amplitude is not related to experimental conditions of reward (one-way ANOVA, F3,41=0.9770, P=0.4129). i, AMPAR/NMDAR ratio onto CeM projectors is similar in unpaired reward and paired reward non learner mice. j, AMPAR/NMDAR ratio of internal capsule inputs onto CeM projectors is significantly increased by food restriction in naïve mice (unpaired t-test t20=2.526, *P=0.0201).
