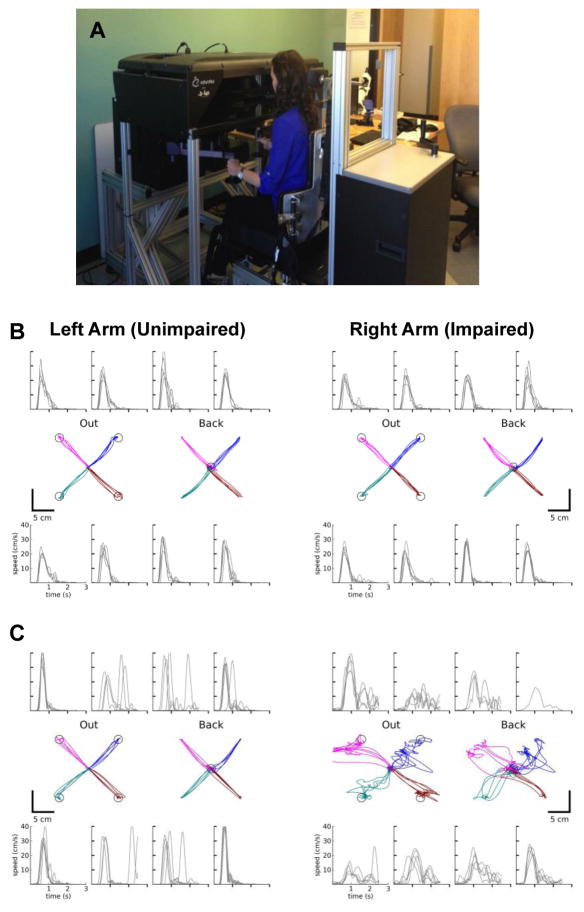
Figure 1.
(a) The robotic apparatus used for the reaching task. (b) Tracings of the reaching movement paths and speeds of a relatively unimpaired subject. (c) Reaching movements and speeds of a patient with one severely impaired and one unimpaired arm. In both (b) and (c), the graphs show time on the x-axis and speed on the y-axis. Below the graphs, the outward paths (from the central location to the outward targets) and return paths (from the outward location back to center) are shown. Circles indicate targets or endpoints of the movements.