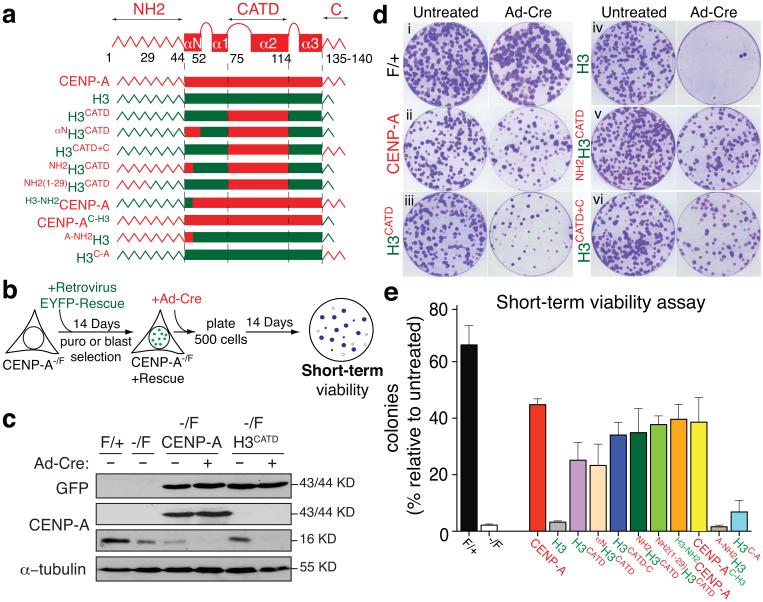
Figure 3.
Short-term rescues of centromere maintenance and function following CENP-A gene depletion. (a) Schematic representation of the rescue constructs. Each CENP-A domain is in red; H3 in green. CENP-A domains and amino acid positions are also indicated. Each construct is tagged with an amino-terminal EYFP (enhanced yellow fluorescent protein) (b) Schematic outlining the construction of cell lines expressing each rescues construct and final clonogenic assay. (c) Immuno-blots of cell extracts with antibodies to GFP, CENP-A and α-tubulin to determine the level of expression of the indicated rescue constructs. (d) Clonogenic survival experiment for the indicated cell lines with or without addition of Ad-Cre. (e) Quantitation of clonogenic assays for each rescue construct shown as the mean of the percentage of Ad-Cre-surviving colonies relative to the untreated condition. Each column represents the average of five independent experiments and error bars represent the SEM. Uncropped image of blots are shown in Supplementary fig. S7.