Fig. 2.
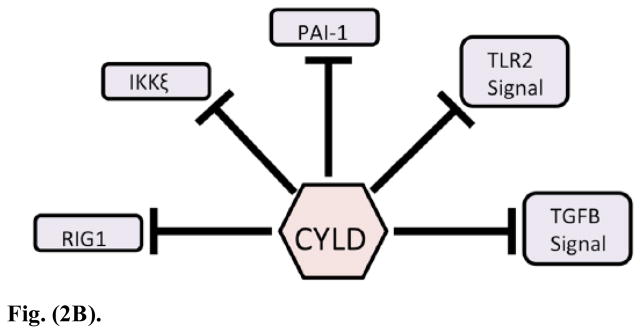
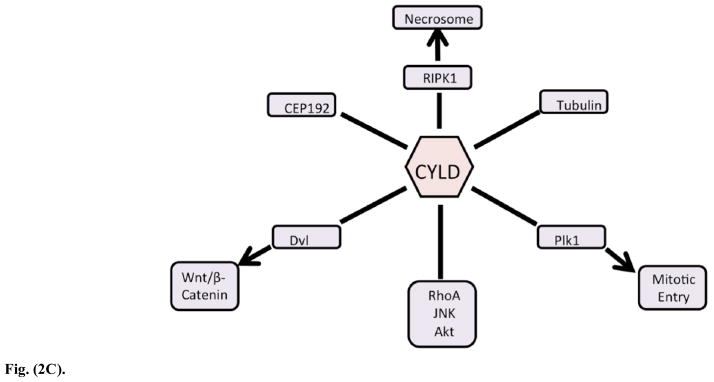
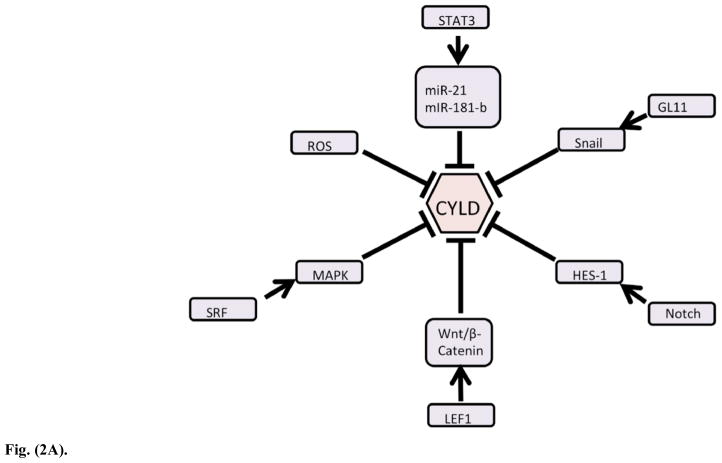
Fig. (2A) The regulation of CYLD is complex and multimodal. As the key effector of K63-linked deubiquitination, which transduces cellular signals, CYLD is tightly regulated at the transcript and protein level, as well as by phosphorylation.
Fig. (2B). CYLD’s regulation of the immune system.
Fig. (2C). CYLD’s interaction with important regulators of necrosis and development.