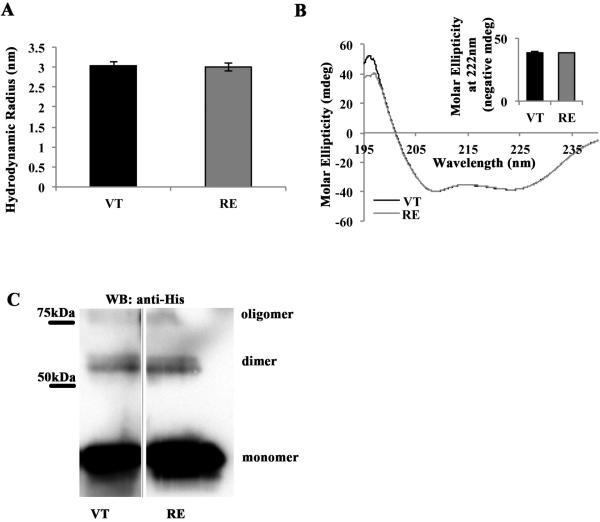
Figure 1. R1049E is structurally similar to wild type VT.
(A) VT and RE have similar size and shape in solution. Solutions of either VT or RE were subjected to Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) analysis, which yields estimates of hydrodynamic radii. Shown is the average hydrodynamic radius predicted from three independent trials of VT and RE, with error bars representing SEM. There is no statistical difference between VT and RE hydrodynamic radii. (B) VT and RE have similar alpha-helical composition. Solutions of VT or RE were subjected to analysis by Circular Dichroism (CD), at wavelengths from 195-240nm. The alpha-helical content of VT and RE is characterized by valleys at 208 and 222nm. Spectra from three independent trials of VT and RE were averaged then set equal at 208nm and graphed. They track almost identically along the entire spectrum of wavelengths examined. The inset panel shows the negative molar ellipticity of VT and RE at 222nm (negative values used for ease of data presentation), which do not differ statistically from one another. (C) VT and RE are crosslinked to a similar degree in solution. Preparations of 15mM VT-His or RE-His in Buffer CL were crosslinked with 100mM disuccinimidyl suberate (DSS) for 30 minutes. Half of the reactions were run on 15% acrylamide gels and blotted with anti-His antibody. Shown are samples from the same western blot. Crosslinked monomer bands are visible below 50kDa, dimer bands are visible just above 50kDa, and the presence of a higher molecular weight oligomer is observed near 75kDa.