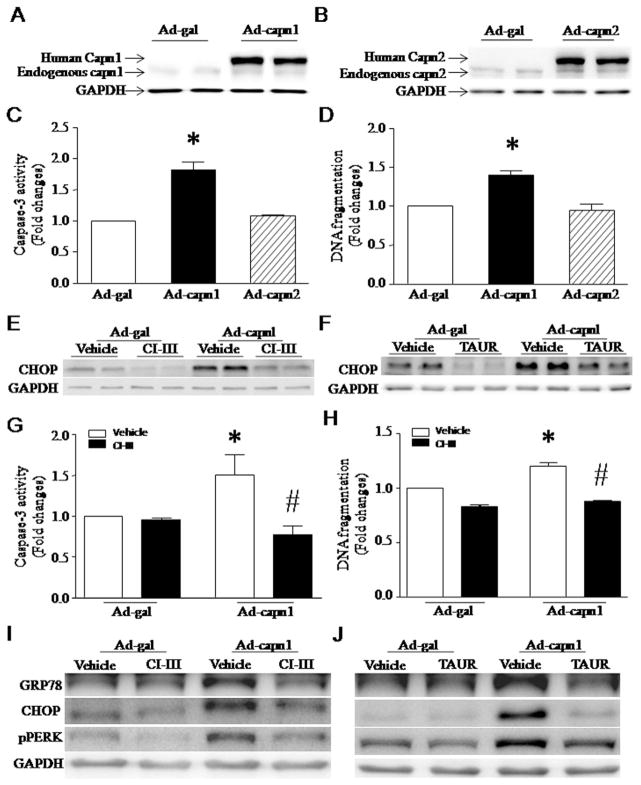
Fig. 1.
Apoptosis and ER stress induced by infection with Ad-capn1. (A–F) Cultured neonatal mouse cardiomyocytes were infected with Ad-capn1, Ad-capn2 or Ad-gal as a control, and then incubated with calpain inhibitor-III (CI-III), TAUR or vehicle. Twenty-four hours later, western blot was performed to analyze capn1, capn2, CHOP and GAPDH proteins, and apoptosis was assessed by measuring caspase-3 activity and DNA fragmentation. (A) A representative western blot for capn1 protein from 3 different experiments. (B) A representative western blot for capn2 protein from 3 different experiments. (C) Caspase-3 activity. (D) DNA fragmentation. (E and F) Representative western blots from 3 different experiments for CHOP and GAPDH proteins. (G and H) H9c2 cells were infected with Ad-capn1 or Ad-gal as a control, and then incubated with CI-III, TAUR or vehicle. Twenty-four hours later, apoptosis was assessed by caspase-3 activity (G) and DNA fragmentation (H). (I and J) Representative western blots from 3 different experiments for GRP78, CHOP, pPERK and GAPDH. Data are mean ± SD from 3 different experiments. *P < 0.05 vs Ad-gal or Ad-gal + Vehicle and #P < 0.05 vs Ad-capn1 + Vehicle.