Fig. 1.
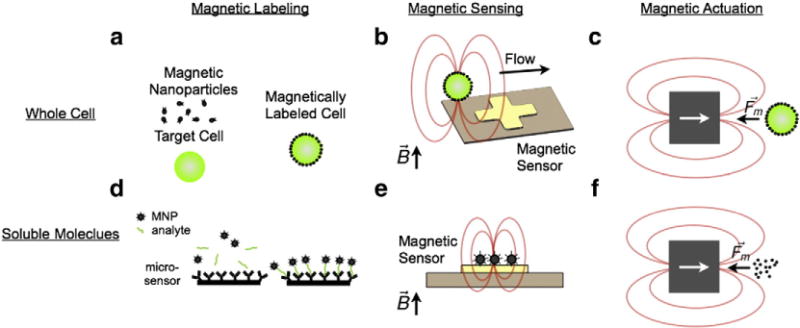
Magnetic sensing and actuation. a. Molecular markers of interest on cells can be labeled with magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs). A cell labeled with MNPs assumes a magnetic moment proportional to the expression of the targeted biomarker. b. Magnetic sensors can be used to quantitatively detect them. c. External magnetic field gradients can be used to apply forces to these cells and d. soluble biomarkers, such as proteinsor nucleic acid, can be captured onto magnetic beads for isolation or detection. For example, shown here a sandwich assay is used to capture an analyte onto a surface, and then label that analyte with MNPs. e. Magnetic sensors can be used to quantify soluble biomarkers labeled with MNPs. f. External magnetic field gradients can be used to isolate magnetic beads that have captured soluble biomarkers.
