Figure 2.
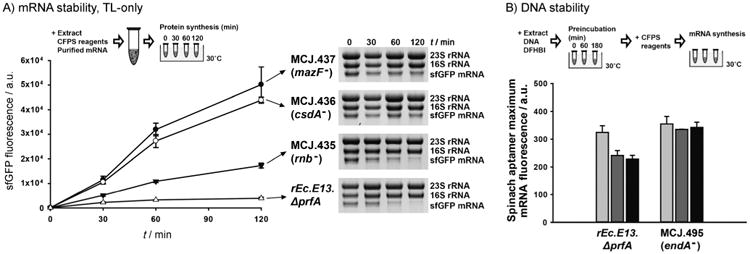
The impact of functionally inactivating nucleases on cell-free transcription and translation. A) Cell-free translation (TL)-only reactions of wild-type sfGFP from purified mRNA in different single RNase-deficient cell extracts. At least three independent reactions for each sample were performed for 120 min at 30°C. sfGFP synthesis was monitored by sfGFP fluorescence (left), and mRNA levels were assessed by an RNA gel (right). B) Cell-free Spinach aptamer synthesis by using endonuclease I-deficient (MCJ.495) and -present (rEc.E13.ΔprfA) extracts. After preincubation (0 (
 ), 60 (
), 60 (
 ), and 180 min (■)) of Spinach aptamer plasmid DNA with cell extract, CFPS reagents were added and incubated at 30°C. Maximum mRNA synthesis levels from the mRNA synthesis time course (Figure S2) were compared. At least three independent reactions for each sample were performed, and one standard deviation is shown.
), and 180 min (■)) of Spinach aptamer plasmid DNA with cell extract, CFPS reagents were added and incubated at 30°C. Maximum mRNA synthesis levels from the mRNA synthesis time course (Figure S2) were compared. At least three independent reactions for each sample were performed, and one standard deviation is shown.
