Figure 4.
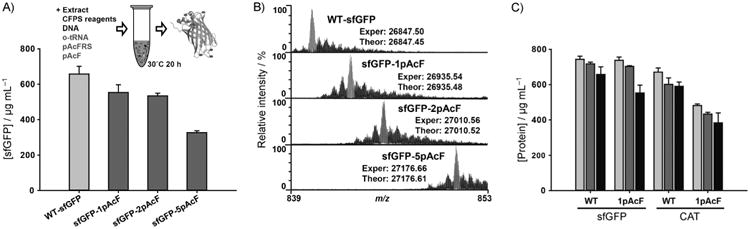
pAcF incorporation at single and multiple amber sites by using the improved cell extract from the MCJ.559 strain. A) Yields of active wild-type sfGFP (WT-sfGFP) and modified sfGFP proteins containing one, two, and five pAcFs. B) Spectrum of the 32+ charge state of sfGFP, obtained by top-down mass spectrometry and illustrating site-specific incorporation of pAcF at single and multiple sites. Major peaks (gray) in each spectrum coincide with the theoretical peaks for each species (Figure S6). “Exper” indicates experimentally obtained protein mass, and “Theor” indicates theoretically calculated protein mass (Table S4). Smaller peaks to the right of the major peaks are due to oxidation of the protein—a common electrochemical reaction occurring during electrospray ionization. Water loss events from the intact sfGFP were detected at minor levels to the left of the major peaks. C) Comparison of total (
 ), soluble (
), soluble (
 ), and active (■) protein yields of sfGFP and CAT with and without single pAcF. At least three independent CFPS reactions for each sample were performed for 20 h at 30°C for (A) and (C), and one standard deviation is shown.
), and active (■) protein yields of sfGFP and CAT with and without single pAcF. At least three independent CFPS reactions for each sample were performed for 20 h at 30°C for (A) and (C), and one standard deviation is shown.
