Fig. 5.
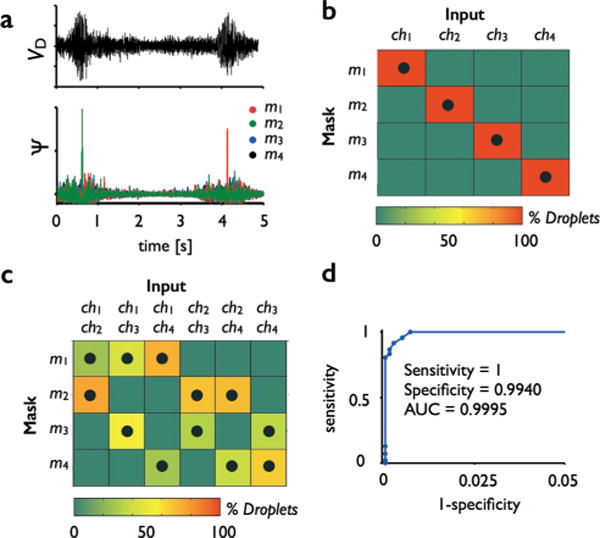
Multi-channel detection. Parallel streams of droplets can be monitored simultaneously by using the unique pattern of each channels’ mask to identify each passing droplet’s channel. a. Two droplets are shown passing in the raw data. After correlation with the set of four masks, the first droplet creates a peak in m2 and the second in m1, allowing their channels to be correctly identified. These curves are the maximum projection of correlations at varying velocity v. b. To test this platform, we passed droplets through each of the four channels and quantified the fraction of droplets measured in each channel in a heat map. Black dots show the channels where droplets were passed. c. We similarly tested the chip’s capability for measuring multiple channels simultaneously, by passing droplets through each of the six possible pairs of channels. d. The sensitivity and specificity was quantified, and summarized on a receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve.
