Fig. 5.
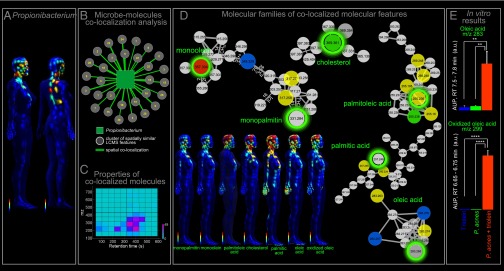
Propionibacterium genus colocalization with lipids on person 2’s body as well as in vitro study of triolein hydrolysis by P. acnes. (A) Topographical maps show the spatial distribution of this genus on the female and male individual. (B) Molecular UPLC-QTOF features spatially colocalized with the Propionibacterium bacterial taxon are displayed as a network, where a square node represents the Propionibacterium taxon, circular nodes represent clusters of tightly colocalized molecular features, and a node represents colocalization between the bacterial taxon map and a molecular cluster map. The number of tightly colocalized molecular features (having nearly identical spatial distributions) is shown inside each circle. In total, 492 molecular features were spatially colocalized with the Propionibacterium taxon. (C) The heat map represents the RT and m/z values of colocalized LC-MS features; most of them have an LC RT of 300–400 s and m/z 200–400 and a region that matches many hydrophobic molecules such as lipids. (D) Molecular networking of molecular families that have similar distribution to the Proprionibacteria and highlights the colocalized MS features and structurally related molecules of the selected molecules (green circle) found in UPLC-QTOF data. (E) In vitro analysis considering P. acnes cultures with or without triolein as well as blank growth media with triolein demonstrate the potential of microbiota to be involved in transformation of large human lipids (e.g., the triacyl glyceride triolein) into smaller lipids and fatty acids as those detected on the skin and colocalized with Propionibacterium (here oleic acid and oxidized oleic acid). Area under the peak calculation of oleic acid and oxidized oleic acid was measured for RT ranges 7.5–7.8 min for m/z 283 and 6.65–6.75 min for m/z 299. The in vitro assay was performed three times (error bars, SD) and can be interpreted as a significant (Student t test, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001) increase of lipid products observed in the presence of P. acnes supplemented with triolein. See also Fig. S7.
