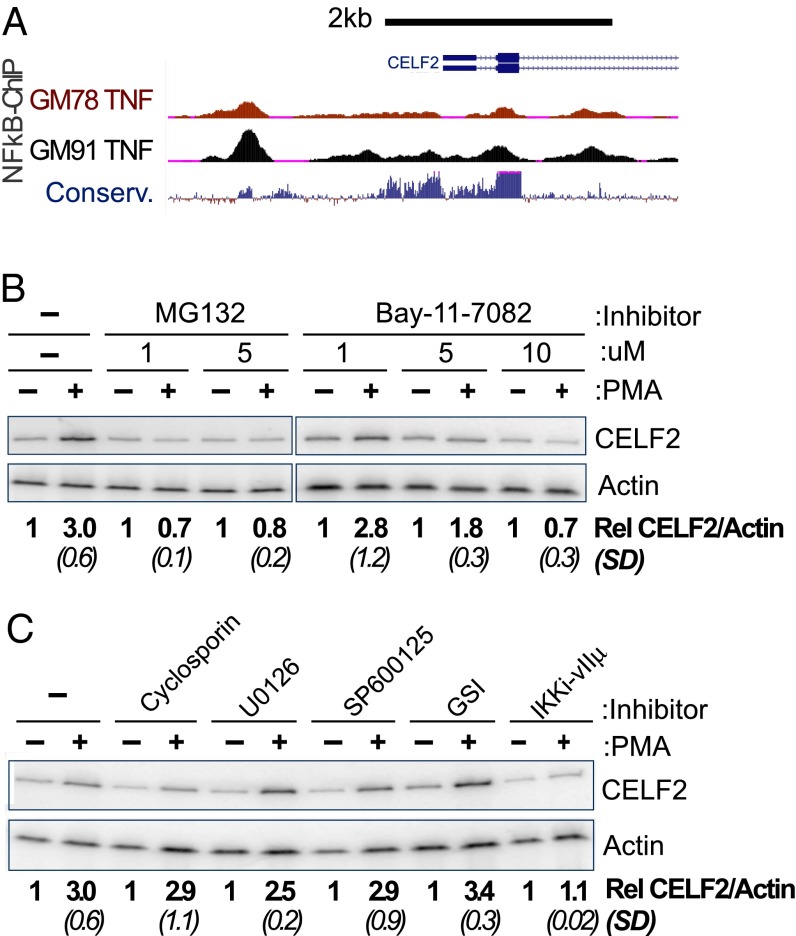
Fig. 2.
Inhibition of NF-κB abrogates the rapid transcriptional induction of CELF2. (A) University of California Santa Cruz Genome Browser shot of 5′ end of the CELF2 locus, showing ChIP signal for NF-κB (RelA) at regions of high conservation upstream of CELF2 transcription start site in TNF-α–induced GM12878 and GM12891 lymphoblastoid cell lines (genome.ucsc.edu/) (68). (B and C) RT-PCR analysis, as in Fig. 1A, showing loss of CELF2 induction upon inhibition of NF-KB (B and C) or other PMA-induced transcription factors (C). Inhibitors are as follows: MG132 (5 μM, inhibits proteosome degradation of IkB), BAY11-702 (10 μM, inhibitor of IkB-a), cyclosporin A (10 μM, inhibits NFAT), U0126 (20 μM, inhibits MEK pathway), SP600125 (50 μM, inhibits JNK activation of AP-1), GSI (1 μM, inhibits Notch activation), IKK inhibitor VII (10 μM, inhibits IKK-mediated degradation of IkB). Induction of CELF2 mRNA is calculated as the fold-increase in CELF2 in PMA treated sample relative to unstimulated control, normalized to actin as a loading control. Values shown are the average of at least three independent experiments. SD are shown in parentheses.