Fig. 2.
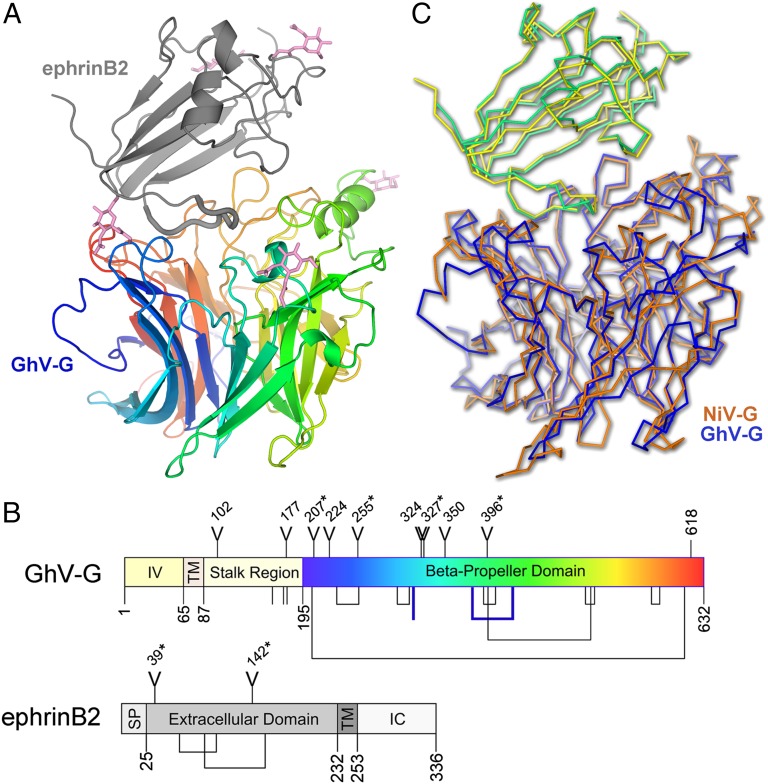
GhV-G and recognition of ephrinB2. (A) Crystal structure of GhV-G in complex with ephrinB2. The six-bladed β-propeller of GhV-G is shown as a rainbow ramped from blue (N terminus) to red (C terminus). The Greek-key fold of ephrinB2 is shown as a gray cartoon. Asparagine-linked N-acetylglucosamine moieties are shown as pink sticks. (B) Domain schematic of GhV-G (Upper) and ephrinB2 (Lower). IV, intravirion domain; TM, transmembrane domain; SP, signal peptide; IC, intracellular domain. Y-shaped symbols designate N-linked glycosylation sites; those sites observed to be occupied in the crystal structure are marked with an asterisk. Lines and connected lines below each diagram correspond to cysteines and disulfide bonds, respectively. A cysteine and a disulfide bond present in GhV-G, but not conserved in NiV- and HeV-G, are highlighted in bold blue. Only cysteines contained in the mature protein and exposed to the oxidizing extracellular environment are annotated. Residues 618–632 in GhV-G were disordered and not built in the crystal structure. Diagrams were produced by using DOG software (Version 2.0; ref. 72). (C) Structural comparison of African and Asiatic HNV-Gs in complex with human ephrinB2. Structures of GhV-G–ephrinB2 (GhV-G, blue; ephrinB2, yellow) and NiV-G–ephrinB2 (NiV-G, orange; ephrinB2, green; PDB ID code 2VSM) are shown in a Cα trace representation superimposed on the viral receptor component of the complexes.