Figure 1. VitC attenuates the isoflurane-induced caspase-3 activation in H4-APP human neuroglioma cells.
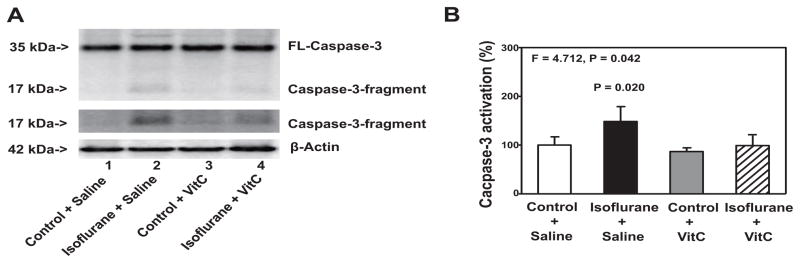
A. The treatment with 2% isoflurane plus saline for six hours (lane 2) induces caspase-3 activation as compared to the control condition plus saline for six hours (lane 1) in the H4-APP cells. The treatment with 400 uM VitC alone (lanes 3) does not induce caspase-3 activation as compared to the control condition plus saline (lanes 1). There is lesser caspase-3 activation following the treatment with 2% isoflurane plus 400 uM VitC for six hours (lane 4) than that following the treatment with 2% isoflurane plus saline for six hours (lane 2). There is no significant difference in the levels of full length caspase-3 and β-Actin among the above treatments. B. The quantification of the Western blots shows that the treatment with 2% isoflurane plus saline for six hours (black bar), but not the control condition plus 400 uM VitC for six hours (gray bar), induces caspase-3 activation as compared to the control condition plus saline for six hours (white bar) in H4-APP cells. The treatment with 400 uM VitC (net bar) attenuates the isoflurane-induced caspase-3 activation (black bar). N = 6 in each group. FL, full length; APP, amyloid precursor protein; VitC, Vitamin C.
