Figure 4. VitC attenuates the isoflurane-induced reduction in MMP in H4-APP cells.
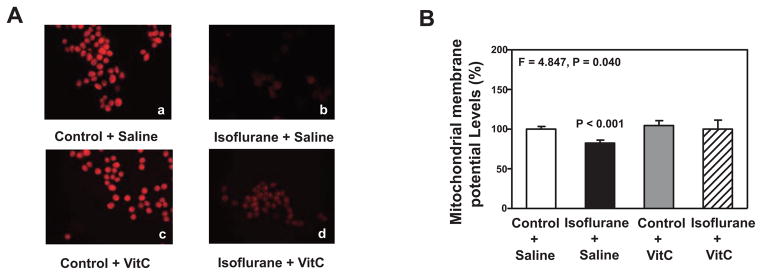
A. Staining of tetramethylrhodamine ethyl ester and perchlorate, the MMP-dependent fluorescent indicator, shows that the treatment with 2% isoflurane plus saline for three hours (b) decreases MMP levels as compared to the control condition plus saline for three hours (a). Treatment with 2% isoflurane plus 400 uM VitC for three hours (d) attenuates the isoflurane-induced MMP reduction (b). B. Tetraethylben-zimidazolylcarbocyanine iodide (JC-1) fluorescence analysis shows that the treatment with 2% isoflurane plus saline for three hours (black bar) decreases the levels of mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) as compared to the control condition plus saline for three hours (white bar) in the H4-APP cells. The treatment with 400 uM VitC for three hours (gray bar) does not significantly alter the MMP levels as compared to the control condition plus saline for three hours (white bar). The treatment with 2% isoflurane plus 400 uM VitC for three hours (net bar) leads to a lesser reduction in MMP levels as compared to the treatment with 2% isoflurane plus saline for three hours (black bar). N = 6 in each group. MMP, Mitochondrial membrane potential; VitC, Vitamin C.
