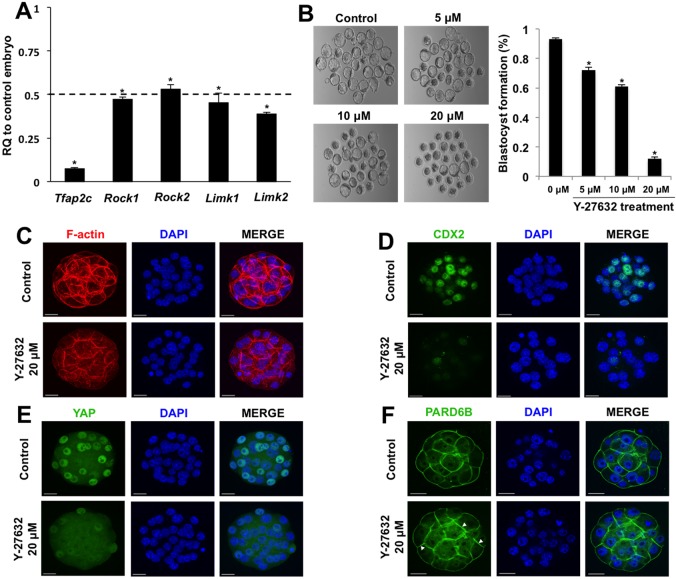
Fig. 6.
TFAP2C regulates position-dependent HIPPO signaling in part via ROCK signaling. (A) Real-time qPCR analysis of Rock1, Rock2, Limk1 and Limk2 transcripts in TFAP2C KD morulae. There was a significant decrease in Rock1, Rock2, Limk1 and Limk2 transcripts in TFAP2C KD morulae. A total of three biological replicates were performed. (B) Treatment of wild-type 8-cell embryos with Y-27632 blocks blastocyst formation in a dose-dependent manner. A total of three biological replicates were performed using 42 embryos in each group. (A,B) *P<0.05. Error bars indicate mean±s.e.m. (C) F-actin organization was disrupted in a subset of embryos treated with 20 μM Y-27632. (D) Cdx2 expression was severely reduced in embryos treated with 20 μM Y-27632. (E) Treatment of embryos with 20 μM Y-27632 activates HIPPO signaling in the outside cells causing loss of YAP in the nuclei. (F) In embryos treated with 20 μM Y-27632, PARD6B was enriched at both the apical and basolateral regions. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. Immunofluorescence experiments were performed using a total of two to three biological replicates with 16-30 embryos per group. In several of the experimental replicates, control and treated embryos were co-stained with phalloidin to visualize F-actin in conjunction with CDX2 and YAP. Scale bars: 20 μm.