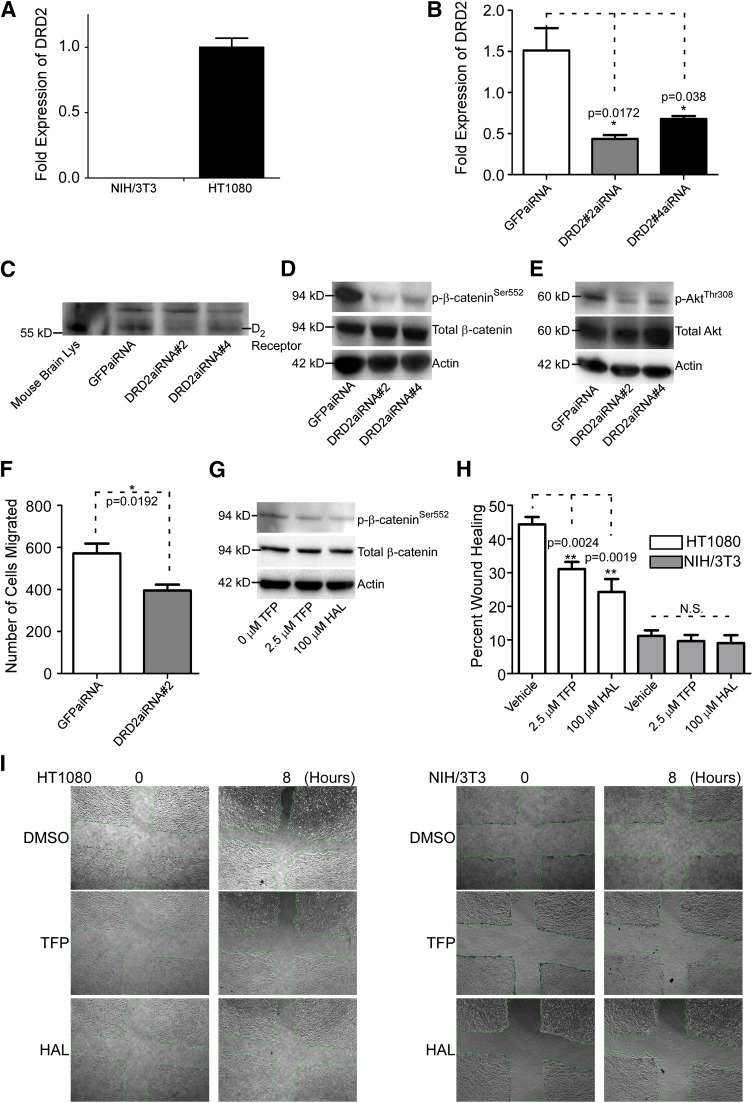
Fig. 5.
Knockdown of DRD2 results in decreased phosphorylated β-cateninSer552 and AKTSer473 and reduced cancer cell migration. (A) Real-time RT-PCR analysis of NIH/3T3 and HT1080 cells reveals that HT1080 cells express a relatively high level of DRD2 mRNA compared with NIH/3T3. The hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HPRT) housekeeping gene was used as a normalization control. The experiment was repeated three times. (B) Silencing of DRD2 by validated aiRNAs in HT1080 cells examined by real-time RT-PCR. The HPRT housekeeping gene was used as a normalization control. The experiment was repeated three times. (C) aiRNA knockdown of DRD2 results in less DRD2 expression examined by Western blot using an anti-DRD2 antibody. Mouse brain lysate was used as a positive control and nonspecific bands were used as loading control. (D) Knockdown of DRD2 results in decreased p-β-cateninSer552 as demonstrated by Western blot analysis using an anti–p-β-cateninSer552 antibody. Total β-catenin and β-actin were used as controls. (E) p-AKTThr308 is reduced when DRD2 is knocked down in HT1080 cells examined by Western blotting using anti–p-AKTThr308 antibody. Total AKT and actin were used as controls. (F) Knockdown of DRD2 results in reduced cancer cell migration in HT1080 cells examined by a two-dimensional dot cell migration assay. (G) Haloperidol, as well as TFP reduced p-β-cateninSer552, examined by Western blotting analysis using an anti–p-β-cateninSer552 antibody. Total β-catenin and β-actin were used as controls. (H) TFP and haloperidol decrease HT1080 cell migration as demonstrated by a wound healing migration assay. There are no effects on NIH/3T3 cells. The experiment was repeated three times. (I) Representative images of wound healing in HT1080 and NIH/3T3 untreated, TFP-treated, and haloperidol-treated cells. GFP, green fluorescent protein; HAL, haloperidol; Lys, lysate.