Figure 2.
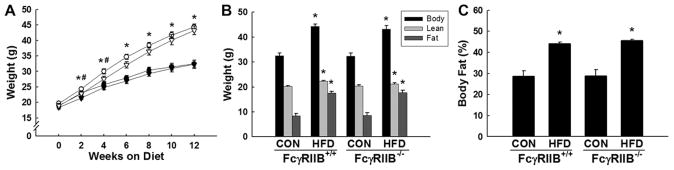
Fcγ receptor IIB (FcγRIIB)+/+ and FcγRIIB−/− mice gain equal weight and fat mass on high-fat diet (HFD). At 5 to 6 weeks of age, FcγRIIB+/+ and FcγRIIB−/− male mice were placed on either a control chow diet (CON) or a HFD. A, Body weight was measured over time in FcγRIIB+/+ CON (●), FcγRIIB+/+ HFD (○), FcγRIIB−/− CON (▼), and FcγRIIB−/− HFD (▽). B and C, After 12 weeks on the respective diets, body weight was measured and lean body mass and fat mass were measured by dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA; B), and percentage body fat was calculated (C). Values are mean±SEM (n=8–12), *P<0.05 vs CON diet, #P<0.05 vs FcγRIIB−/− HFD.
