Figure 1.
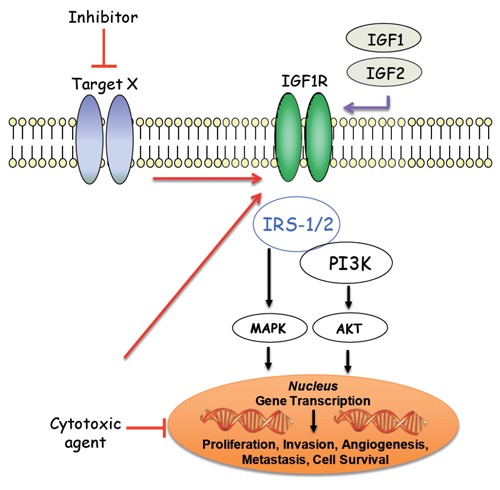
The insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R), a transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinase, is activated by its cognate ligands, insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and -2 (IGF-2), resulting in receptor auto-transphosphorylation and signaling cascades that progress through the IRS-l/PI3K/AKT and MAPK pathways. Stimulation of both pathways ultimately leads to various cancer promoting phenotypes including cellular proliferation, survival, invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis. Specific IGF-1R mediated activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway results in a pro-survival signal that has been shown to promote resistance to both chemotherapy-induced apoptosis or to molecular targeted therapies (Target X).
