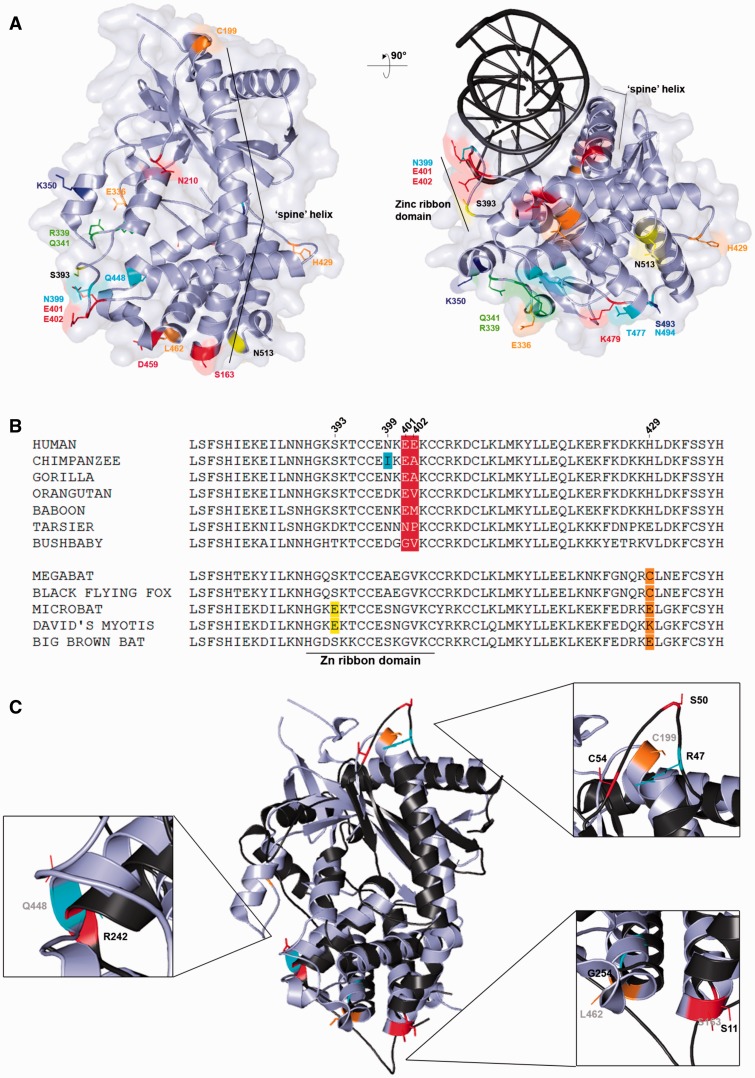
Fig. 5.—
(A) Positively selected sites mapped onto the human cGAS structure (PDB code: 4O67).Color codes are as follows: Red, positively selected sites in the primate phylogeny; orange, positively selected sites in the bat phylogeny; yellow, lineage-specific sites; cyan, positively selected sites in the chimpanzee lineage; blue, positively selected sites in the gorilla lineage; green, positively selected sites in more than one lineage among human, chimpanzee, and gorilla. The cGAS–dsDNA complex was obtained by superimposing the human cGAS structure (PDB code: 4O67) with the porcine cGAS–dsDNA complex. The porcine cGAS structure is omitted. (B) Multiple alignment of cGAS amino acids 377–437 (a portion of the sequence encompassing the zinc ribbon domain) for a few of representative primates and bats species. (C) Superimposition of the structure of the cGAS (PDB code: 4O67, light gray) and OAS1 (PDB code: 4IG8, black). Enlargements highlight positively selected sites located in the corresponding regions of the two different enzymes. Color codes are as in (A).