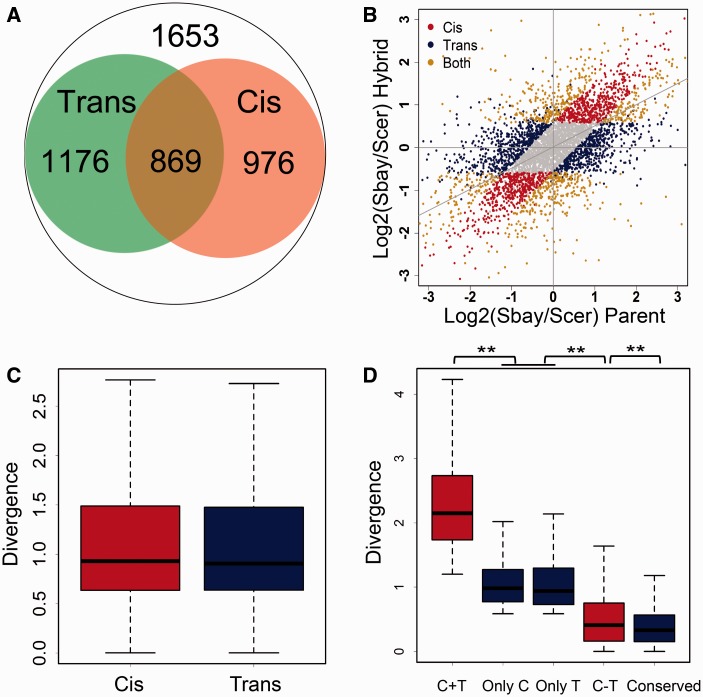
Fig. 4.—
The cis and trans effects on the evolution of gene transcription. (A) The cis effect was defined by comparing the transcription difference between alleles in the hybrid strain (FDR ≤ 0.05 and fold change ≥1.5, 1,845 genes in total). The trans effect was defined by measuring the ratio change of allelic transcription between the parental strains and the hybrid (2,045 genes). The overlapping genes from the two categories are those that have both the cis and trans effects (869 genes). (B) Scatter plot for the cis, trans and CT genes in transcription regulation. The gray points show genes without allelic transcription divergence (FDR > 0.05 or fold change <1.5), and the gray diagonal line represents the linear fitting using all the data. (C) Boxplot for the transcription divergence between the parental strains for the cis and trans genes. The cis and trans effects have similar contributions to the magnitude of transcription divergence (median divergencecis = 0.93, divergencetrans = 0.91, P = 0.34). (D) Boxplot for the transcription divergence between the parental strains for the only cis, the only trans, the enhancing CT (C + T), the compensatory CT (C − T), and the conserved genes. The ** means P < 1.50E−6.