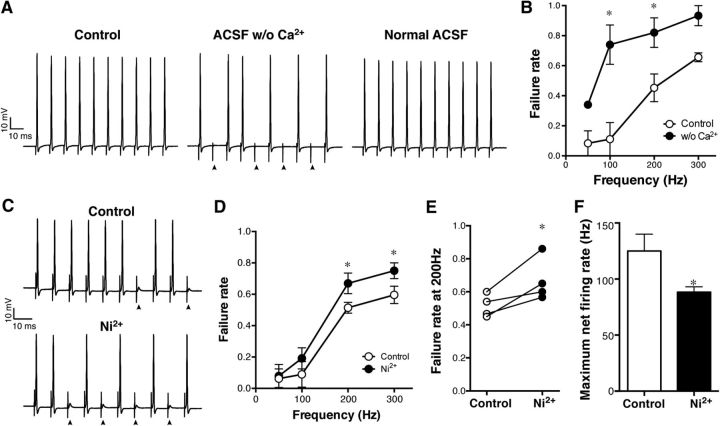
Figure 7.
Increased failure of antidromic APs by inhibiting Ca2+ influx. A, The failure of antidromic APs was also increased by applying ACSF with no Ca2+ (ACSF w/o Ca2+) to the axon. This effect was reversed in normal ACSF (Normal ACSF). B, Pooled data (n = 3). *p = 0.001 (at 100 Hz) and 0.019 (at 200 Hz). C, Similar increase in the failure rate induced by Ni2+. Ni2+ at 100 μm was applied to the axon for 5 min. D, Pooled data (n = 4). *p = 0.03. E, The failure rate at 200 Hz stimulation before and after the Ni2+ application. p = 0.04. F, Decrease of the maximum net firing rate after the Ni2+ treatment. *p = 0.04.