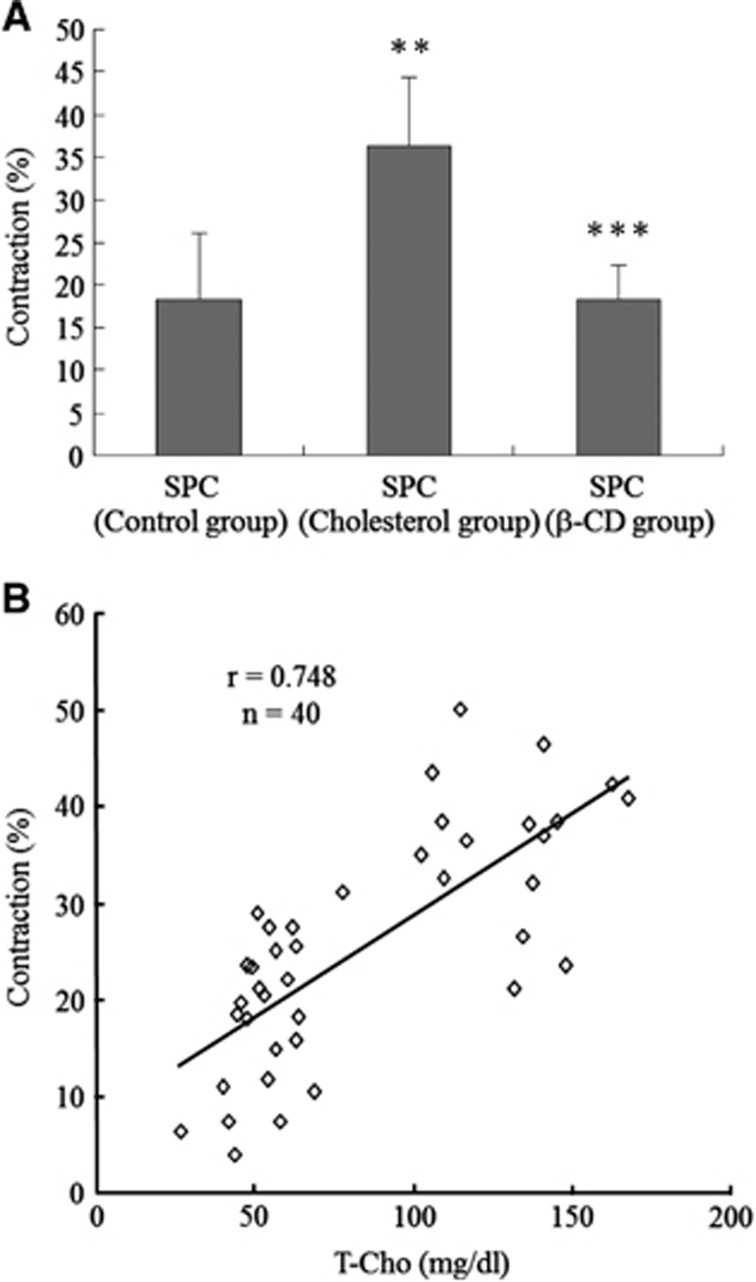
Figure 2.
Link between cholesterol and sphingosylphosphorylcholine (SPC)-induced vascular smooth muscle (VSM) contraction. (A) SPC (100 μmol/L)-induced contraction in rats in the control group (n=24) was increased in those fed a 1% cholesterol diet (cholesterol group, n=16). SPC (100 μmol/L)-induced contraction in animals fed a 1% cholesterol diet was reduced in those fed a 1% cholesterol+5% β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) diet (β-CD group, n=5). (B) The extent of contraction correlated (r=0.75, n=40) with serum T-Cho levels. Values are shown as means+s.d. **P<0.001 versus control group. ***P<0.01 versus cholesterol group.