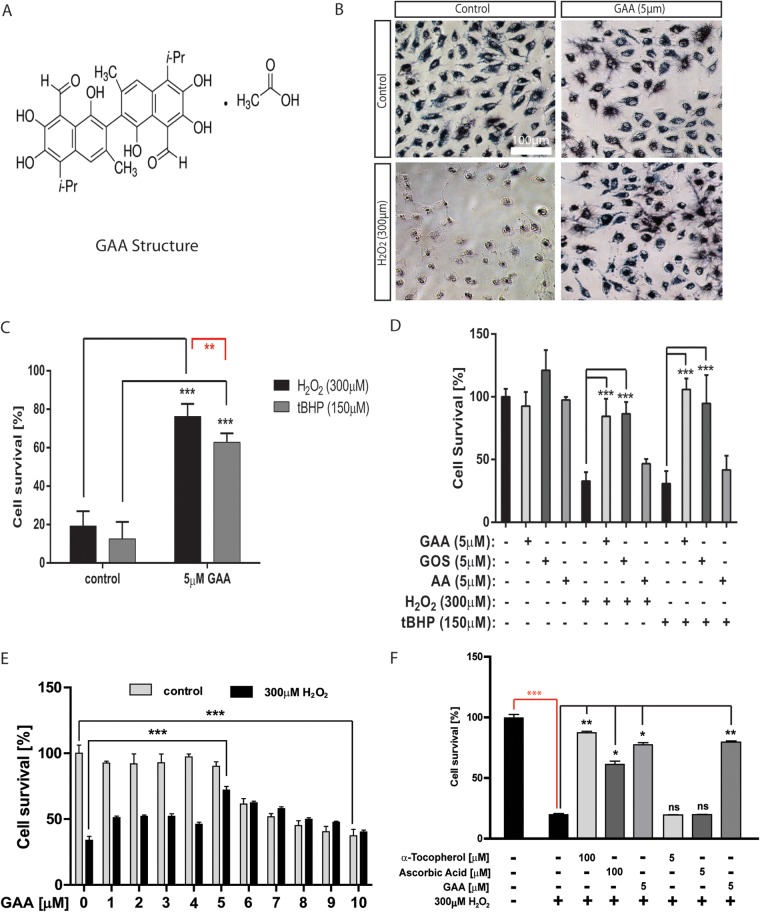
FIG 2.
GAA protects ARPE-19 cells from oxidative stress-induced cell death. (A) Chemical structure of gossypol acetic acid (GAA). (B) Representative MTT pictures showing GAA protects ARPE-19 cells from H2O2-induced cell death. (C) Comparison of ARPE-19 cell survival upon pretreatment with GAA and then with 300 μM H2O2 or 150 μM tBHP. (D) Comparison of cell protective abilities of gossypol acetic acid (GAA), gossypol (GOS), and acetic acid (AA). Cells treated with 5 μM concentrations of each compound were exposed to H2O2 or tBHP. Cell survival was evaluated by MTT assay. (E) Analysis of GAA protective effect on RPE cells under different GAA concentrations. Cells were pretreated for 24 h with different concentrations of GAA and treated with H2O2. (F) Comparison of GAA protective ability with other established indirect antioxidants: vitamin E (α-tocopherol) and vitamin C (ascorbic acid). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.