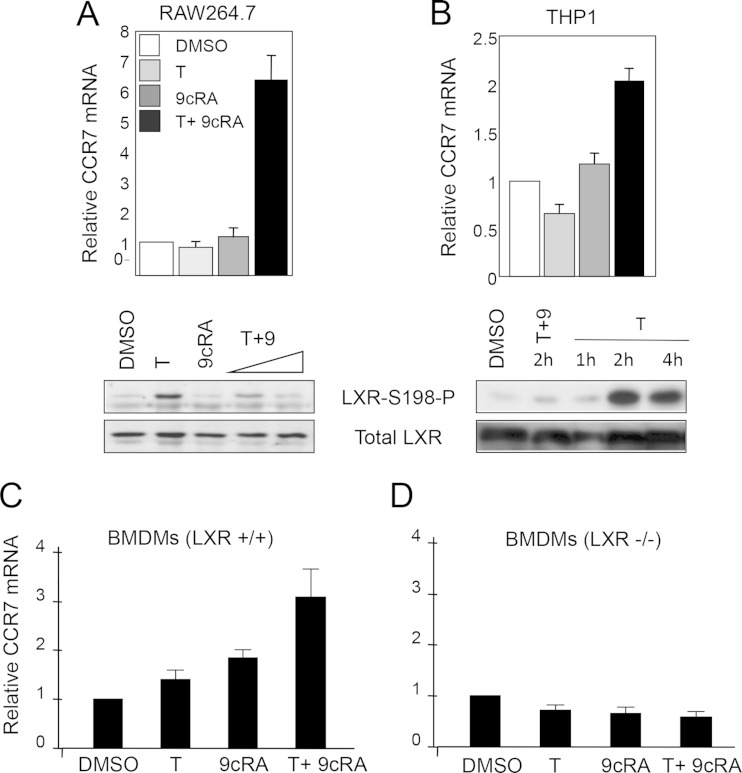
FIG 2.
RXR ligand 9-cis-retinoic acid inhibits LXRα phosphorylation and induces Ccr7 expression. (A) (Top panel) Ccr7 expression was analyzed by qPCR in RAW264.7 cells expressing WT LXRα in the absence of ligand (DMSO) and in the presence of T0901317 (T; 5 μM) or 9-cis-retinoic acid (9cRA; 1 μM) or upon cotreatment with both T (5 μM) and 9cRA (1 μM) for 24 h. The values indicate expression levels normalized to cyclophilin A mRNA levels and are presented relative to the expression in vehicle-treated cells, which was set as 1. Error bars represent standard deviations (SD). (Bottom panel) Nuclear extracts were prepared from RAW-LXRα WT cells cultured for 4 h in the absence (DMSO) or presence of T (5 μM) or 9cRA (1 μM) or a combination of T (5 μM) and increasing (0.1 and 1 μM) concentrations of 9cRA. LXRα S198 phosphorylation and the total level of LXRα were detected by Western blotting. (B) (Top panel) Ccr7 expression was analyzed by qPCR in differentiated THP1 cells treated as described for panel A. Values were normalized to GAPDH gene levels. (Bottom panel) Nuclear extracts from THP1 cells were analyzed for T-dependent LXRα S198 phosphorylation over a 4-h time course and in the presence of a 2-h 9cRA (1 μM) cotreatment. (C and D) LXR functions as an activator of Ccr7 mRNA expression. Bone marrow-derived macrophages were isolated from Lxr+/+ and Lxrα/β−/− mice. Cells were treated in culture with the vehicle (DMSO), T (5 μM), 9cRA (1 μM), or both ligands for 18 h, and Ccr7 mRNA expression normalized to cyclophilin A levels was analyzed by qPCR; data are presented relative to the expression in vehicle-treated cells, which was set as 1. Error bars represent SD.