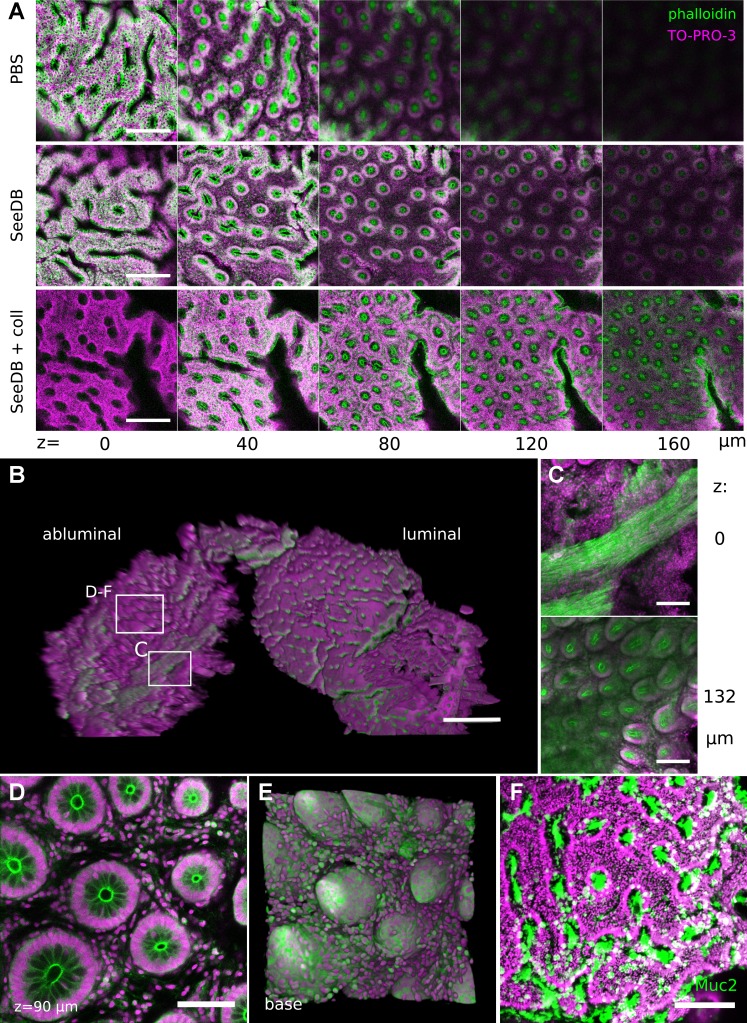
Fig. 9.
DMI provided a 3D view of human colonic biopsies. A: treatment of fixed human biopsy samples with SeeDB or SeeDB with collagenase improved optical penetration in luminal images. B: 3D projection shows the structure of a SeeDB-cleared biopsy sample, including both luminal and basilar planes. Boxes indicate regions highlighted. C: crypt structures were resolved through a layer of muscle in abluminal images. D and E: abluminal images permitted reconstruction of the crypt base in single z planes (D) and 3D basilar (E) shape displays. F: immunohistochemical staining for MUC2 could be performed to identify goblet cells on the luminal surface of human biopsies. Scale bars: 200 (A), 500 (B), 150 (C), 75 (D), and 150 (F) μm. TO-PRO-3 stained cellular nuclei; phalloidin-DyLight 488 stained actin filaments.