Figure 1.
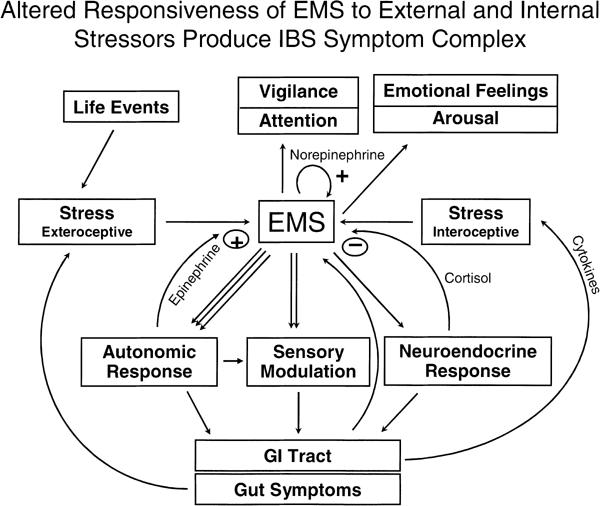
The Emotional Motor System. The EMS refers to a parallel set of outputs from limbic and paralimbic circuits, which generate distinct patterns of body functions (‘body map’) associated with specific emotions (fear, anger, joy, etc). These outputs occur in the form of autonomic nervous system responses, sensory modulations and HPA axis responses. Feedback from the body to the EMS in the form of afferent nerve signals and neuroendocrine signals modify EMS responses. Ascending outputs to cortical regions of the brain generate patterns of vigilance, arousal and attention. The conscious perception of emotional feelings may or may not be associated with activities of the EMS (modified from Mayer et al. 2001) (44).
