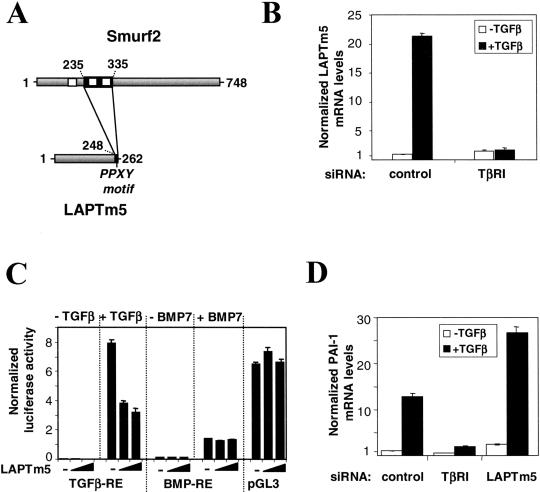
Figure 4.
Involvement of LAPTm5 in the TGFβ pathway. (A) Interaction between Smurf2 and LAPTm5. The full-length proteins are represented in gray; black boxes correspond to the interaction domains. Positions are indicated in amino acids. White boxes correspond to WW motifs in Smurf2. The PPXY motif of LAPTm5 is indicated. (B) Endogenous levels of LAPTm5 mRNA were determined in HepG2 cells by Q-PCR in the absence (white) and the presence (black) of TGFβ for 18 h with or without a TβRI–targeting siRNA duplex. (C) The effect of LAPTm5 overproduction was studied using the following luciferase reporter vectors: a TGFβ-responsive element (TGFβ-RE), a BMP-responsive element (BMP-RE), and an unrelated reporter (pGL3 control). The effect was measured in the presence and the absence of TGFβ or BMP7. HepG2 cells were transfected with 0, 2, or 10 ng of pV3-LAPTm5. The specific luciferase activity was normalized using the pRL-TK vector. (D) Following siRNA-mediated cellular knock-down targeting TβRI and LAPTm5, Q-PCR was used to analyze the endogenous levels of PAI-1 mRNA both in untreated (white) and TGFβ-treated (black) HepG2 cells. mRNA levels were normalized according to an internal GUS control. All results are mean values ±SE calculated from triplicates performed in at least two independent experiments.