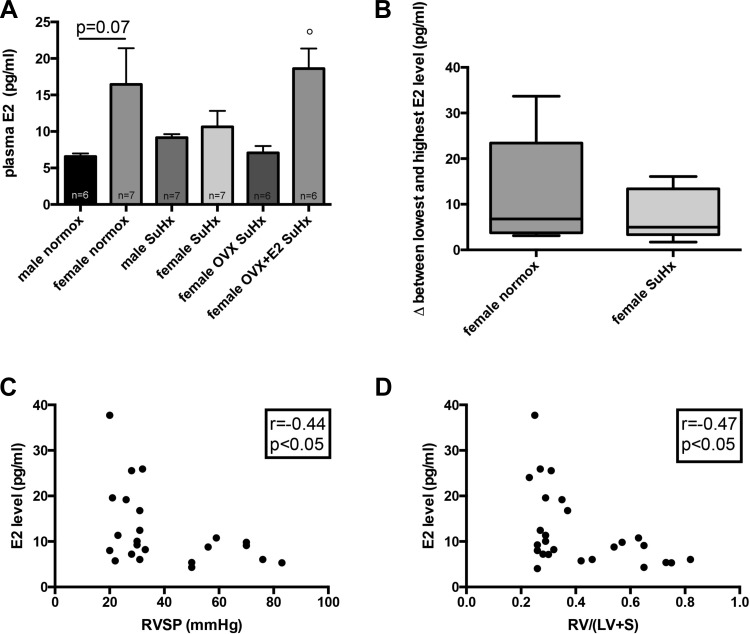
Fig. 5.
Plasma E2 levels in SuHx-PH. Effects of sex, OVX, and E2 repletion in OVX rats on plasma E2 levels in SuHx-PH rats are shown in A. Plasma E2 levels were measured by Calbiotech E2 ELISA. SuHx exposure, OVX, and E2 repletion were as outlined in Fig. 1. Male and female rats exposed to neither Su5416 nor hypoxia served as controls. Values are means ± SE. °P < 0.05 vs. female OVX SuHx (1-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey's test). B: box-and-whiskers plots of distribution of plasma E2 levels in healthy control females and in intact SuHx rats. In each group (n, 6/group), the difference (Δ) between each measured E2 level and the lowest E2 level in that group was calculated and plotted on the y-axis. Boxes represent 25th, 50th, and 75th percentiles; whiskers represent minimum and maximum E2 levels for that particular group. Note strong tendency for higher Δ in control rats compared with SuHx rats. C and D: correlations between plasma E2 levels and RV hypertrophy (determined by Fulton index; see Fig. 2A) and RVSP (see Fig. 2B) in female animals. Data points represent individual animals. Rats from the 4 female treatment groups were included in the analyses. Pearson correlation coefficients and levels of significance are shown in the boxes at top right of each panel. Note inverse relationship between plasma E2 and RV hypertrophy and RVSP, respectively.