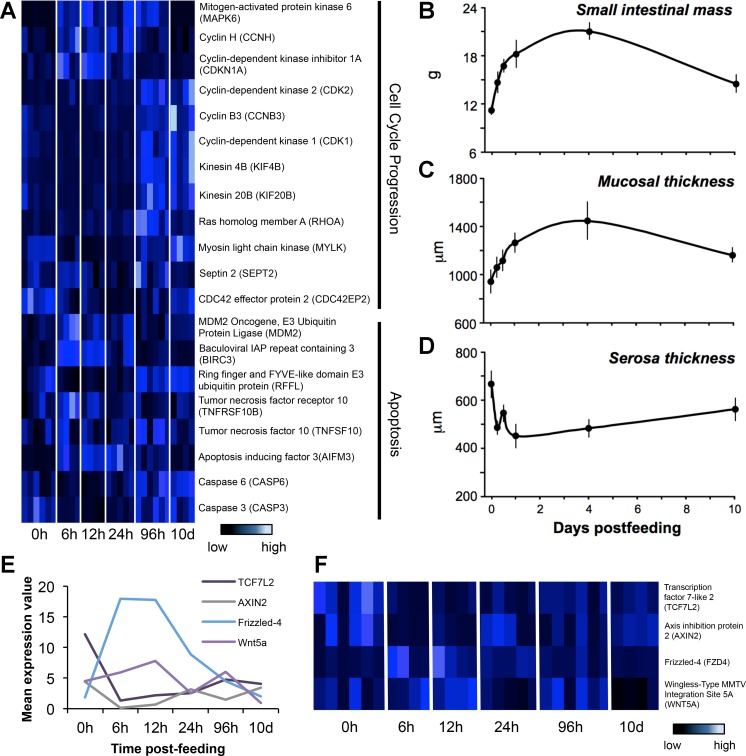
Fig. 4.
Patterns of expression for genes involved in cell cycling, apoptosis, and WNT signaling along with corresponding physiological changes in the small intestine. A: heat-map of genes involved in cell cycle progression and apoptosis that were shown to be significantly differentially expressed across time-points, identified from pairwise and regression analysis. B: change in small intestinal mass across time. C: change in mucosal thickness across time. D: change in serosa thickness across time. E: average expression values for Wnt signaling genes plotted across postfed time-points. F: heat-map of expression values for all replicates across postfed time-points, with each row representing a gene and each column representing an individual, which are manually clustered by time-points. This pathway is known to be important in development and processes such as asymmetric cell division.