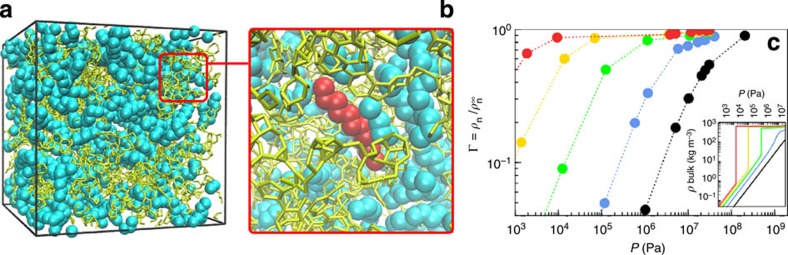
Figure 1. Hydrocarbons in kerogen-like nanoporous carbon under reservoir conditions.
(a) System setup: n-alkanes adsorbed in a porous carbon matrix (volume (5 nm)3); (b) zoom on one dodecane molecule (red) with its neighbours and the surrounding carbon structure; (c) adsorption isotherms of methane (black), propane (blue), hexane (green), nonane (yellow) and dodecane (red), normalized by the maximum density 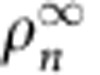 reached at high pressures; the mass density
reached at high pressures; the mass density 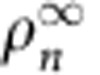 increases slightly with the alkane length (see Supplementary Methods and Supplementary Fig. 2). Because of the small pore sizes (∼1 nm), the system is dominated by fluid/solid interfaces, and the fluid is in a supercritical phase, that is, no gas–liquid phase transition occurs. Inset: bulk phase diagrams for comparison.
increases slightly with the alkane length (see Supplementary Methods and Supplementary Fig. 2). Because of the small pore sizes (∼1 nm), the system is dominated by fluid/solid interfaces, and the fluid is in a supercritical phase, that is, no gas–liquid phase transition occurs. Inset: bulk phase diagrams for comparison.