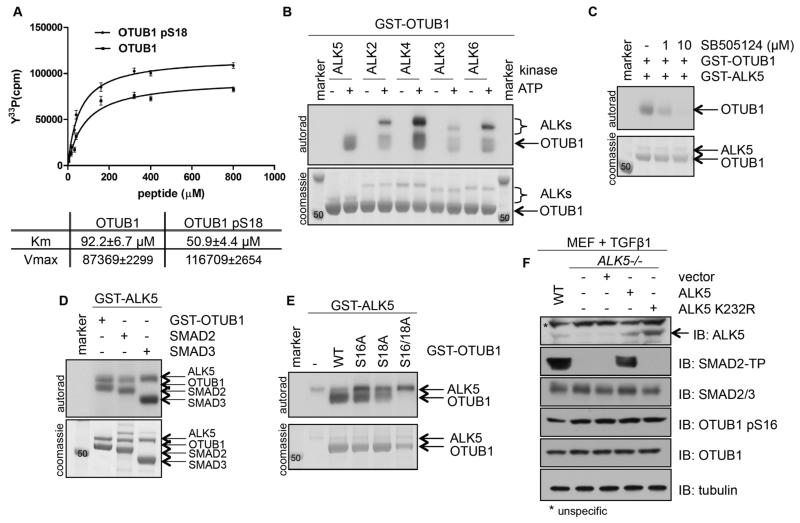
Figure 2. ALKs can phosphorylate OTUB1, but phosphorylation of OTUB1 at Ser16 is specific to CK2.
(A) Kinetics of an in vitro kinase assay assessing CK2α-mediated phosphorylation of increasing amounts of OTUB1 and pSer18-OTUB1 peptides. The Km and Vmax values are indicated. Data are mean ± S.D. from 3 experiments. (B) Coomassie stain and autoradiography of an in vitro kinase assay with different ALKs and GST-OTUB1. (C) As in (B), with GST-ALK5 and GST-OTUB1 in the presence of increasing amounts of the ALK5 inhibitor SB505124. (D) As in (B), with GST-ALK5 and SMAD2, SMAD3 and GST-OTUB1. (E) As in (B), with GST-ALK5 and wild-type or mutant GST-OTUB1. (F) Western blotting (IB) for the indicated proteins in lysates from MEF cells (wild-type, ALK5−/− and ALK5−/− transfected with wild-type or kinase-deficient mutant ALK5) treated with TGFβ (50 pM, 1 hour). (SMAD2-TP: SMAD2 tail phosphorylated at residues Ser465 and Ser467). All blots are representative of 3 independent experiments.