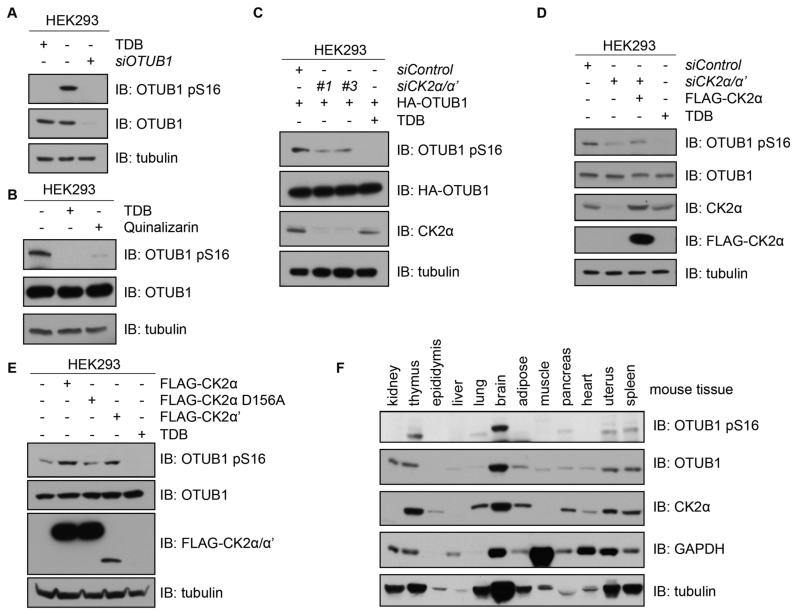
Figure 3. CK2 phosphorylates OTUB1 in vivo.
(A) Western blotting (IB) of lysates from HEK293 cells that were untreated, treated with TDB (10 μM, 4 hours) or transfected with OTUB1 siRNA and lysed 48 hours later. (B) Western blotting (IB) of lysates from HEK293 cells that were untreated or, treated with TDB (10 μM, 4 hours) or quinalizarin (10 μM, 4 hours). (C) Western blotting (IB) of lysates from HEK293 cells transfected with HA-OTUB1 and FOXO4 siRNA (siControl) or one of two siRNAs against both CK2α and CK2α’ splice variants. A separate culture of cells was treated with TDB (10 μM, 4 hours). (D) Western blotting (IB) of lysates from HEK293 cells transfected with FOXO4 siRNA (control) or CK2α/α’ siRNA alone or reconstituted with N-terminal FLAG-tagged CK2α. A separate culture of cells was treated with TDB (10 μM, 4 hours) prior to lysis. (E) Western blotting (IB) of lysates from HEK293 cells transfected with vectors encoding N-terminal FLAG-tagged CK2α, FLAG-CK2α[D156A] or FLAG-CK2α’, or treated with TDB (10 μM, 4 hours). (F) Western blotting of homogenized lysates from the indicated mouse tissues. All blots are representative of 3 independent experiments.