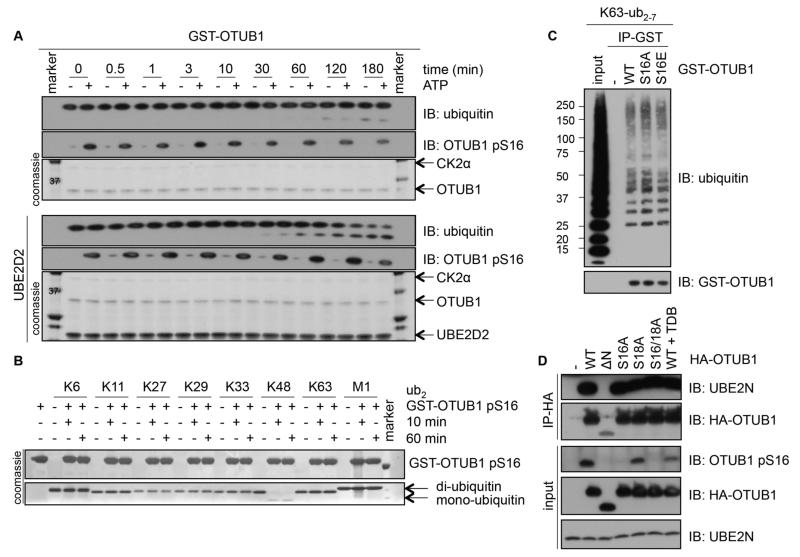
Figure 4. The catalytic activity, ubiquitin- or E2-binding ability of OTUB1 are not altered by OTUB1 Ser16 phosphorylation.
(A) A time course of K48-diubiquitin cleavage assay using unphosphorylated or in vitro CK2-phosphorylated OTUB1 (0.5 μM), in the absence (top panel) or presence of UBE2D2 (bottom panel). Coomassie stains of OTUB1, CK2α and UBE2D2 or Western blotting (IB) of ubiquitin and the phosphorylation of OTUB1 at Ser16 (pS16) are indicated. (B) As in (A), with phosphorylated GST-OTUB1 (5 μM) incubated with K6-, K11-, K27-, K29-, K33-, K48-, K63-, or M1-di-ubiquitin chains for 10 and 60 min in the absence of UBE2D2 and Coomassie stains indicated. (C) Western blotting (IB) of GST (-), GST-OTUB1 (WT), GST-OTUB1-S16A (S16A) or GST-OTUB1-S16E (S16E) incubated in vitro with K63-linked polyubiquitin chains in an interaction assay. (D) Western blotting (IB) of lysates or HA-immunoprecipitates from HEK293 cells transfected with HA-OTUB1 or HA-OTUB1 mutants treated with or without TDB (10 μM, 4 h). All blots are representative of 3 independent experiments.