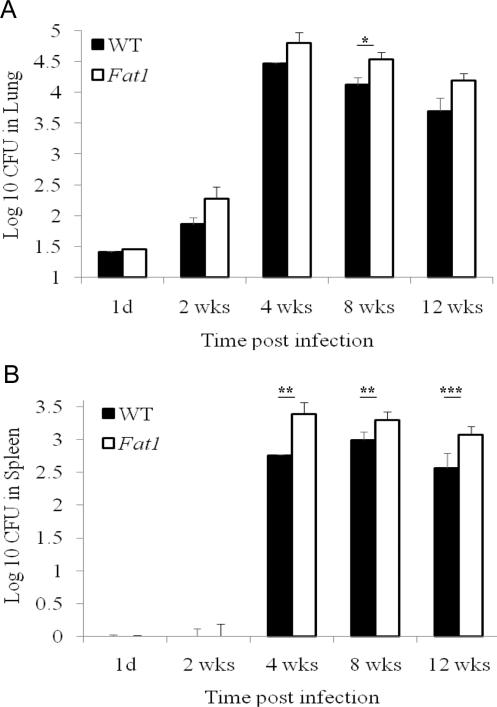
Figure 1.
Increased bacterial loads in fat-1 mice. Animals were infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis via aerosol infection. At 1 day and at 2, 4, 8, and 12 weeks, mice were euthanized, and the numbers of viable bacteria in lung and spleen were determined. Bacterial counts were estimated by the colony forming unit (CFU) assay, as described in the Materials and Methods. Data show bacterial survival as log10 CFU (mean ± standard error of the mean) in fat-1 (dashed line) versus wild-type (WT) mice (solid line). *P < .005; **P < .05; ***P < .01.