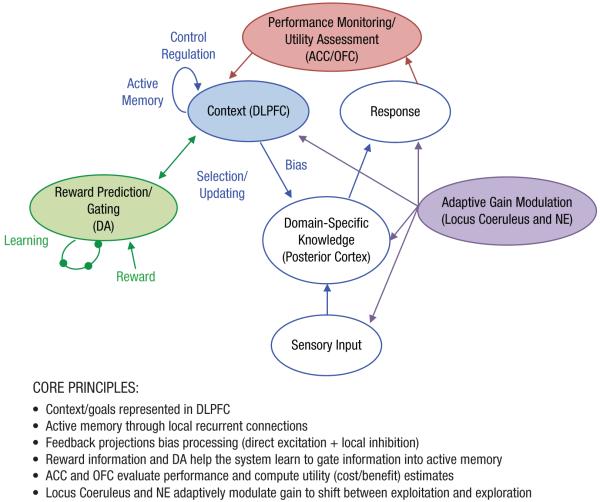
Fig. 4.
Computational model of cognitive control. Extensions to original model developed by Cohen and Servan-Schreiber (1992; model components in blue) that include roles for (a) dopamine (DA) in gating information into active memory (model components in green; Braver & Cohen, 1999), (b) anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) in monitoring for conflict and dynamically regulating cognitive control (model components in red; Botvinick, Braver, Barch, Carter, & Cohen, 2001), and (c) orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) in computing value/utility estimates and the locus coeruleus and norepinephrine (NE) in adaptive gain modulation to shift between exploitation and exploration (model components in purple; Aston-Jones & Cohen, 2005). DLPFC = dorsolateral prefrontal cortex.