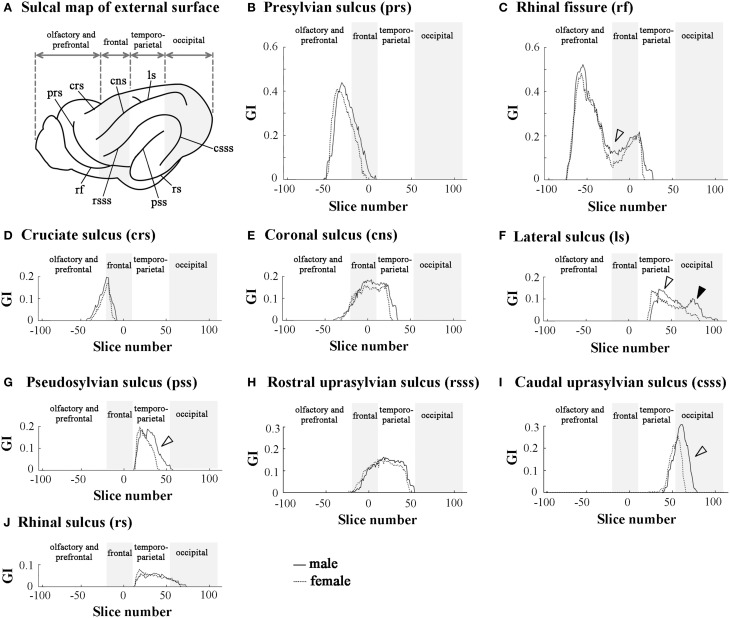
Figure 4.
Rostrocaudal distribution patterns of primary sulcal infolding on external surface of cerebral hemisphere. (A) Sulcal map of the external cerebral surface. (B) Rostrocaudal pattern of the GI of presylvian sulcus infolding (prs). (C) Rostrocaudal pattern of the GI of rhinal fissure infolding (rf). Open arrowhead indicates the rf region, which is more infolded in males than in females. (D) Rostrocaudal pattern of the GI of cruciate sulcus infolding (crs). (E) Rostrocaudal pattern of the GI of coronal sulcus infolding (cns). (F) Rostrocaudal pattern of the GI of lateral sulcus of infolding (ls). Open arrowhead indicates the ls region, which is extended more posteriorly in males than in females in temporo-parietal region, and closed arrowhead indicates the second peak of the ls infolding, which is obvious in males but obscure in females in the occipital region. (G) Rostrocaudal pattern of the GI of pseudosylvian sulcus infolding (pss). Open arrowhead indicates the pss region, which is extended more posteriorly in males than in females in the temporo-parietal region. (H) Rostrocaudal pattern of the GI of rostral suprasylvian sulcus infolding (rsss). (I) Rostrocaudal pattern of the GI of caudal suprasylvian sulcus infolding (csss). Open arrowhead indicates the csss region, which is extended more posteriorly in males than in females in the occipital region. (J) Rostrocaudal pattern of the GI of rhinal sulcus infolding (rs). On the rostrocaudal distribution maps of each measurement, the coronal MRI slice at the anterior commissure (ac) is registered as “slice number 0.” The means of each perimeter are calculated on all coronal MRI slices, and the rostrocaudal course of the distributions of each perimeter is represented throughout the cerebral cortex. Four subdivisions of the cerebral hemisphere, the boundaries of which are defined on the basis of the structural landmarks on coronal MRI images, are indicated by shadows.