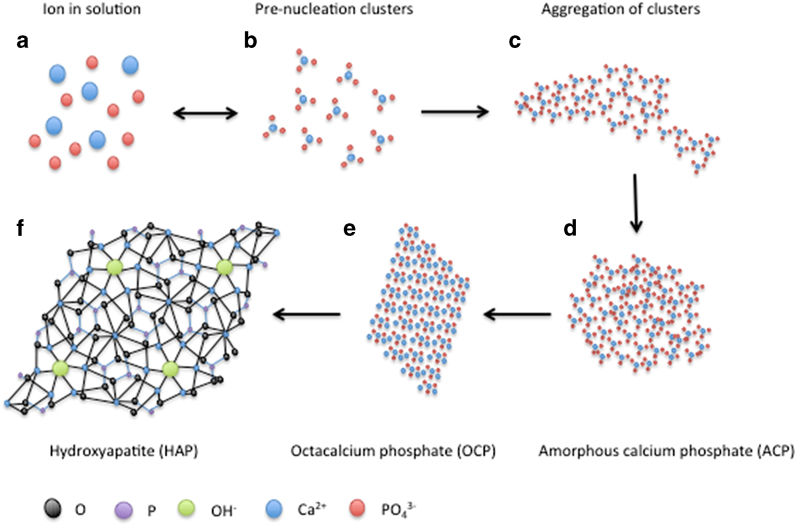
Figure 1.
The pathway of hydroxyapatite formation. Adapted from Habraken et al.22 with permission. A model of hydroxyapatite formation from PNC in solution. Free ions in solution (a) are in equilibrium with Ca triphosphate PNC (b). PNC aggregates (c), which then coalesce to become an ACP nucleus (d). With the addition of Ca ions and the loss of hydrogen ions, ACP transforms into OCP (e) and subsequently HAP (f), the most thermodynamically favourable state.