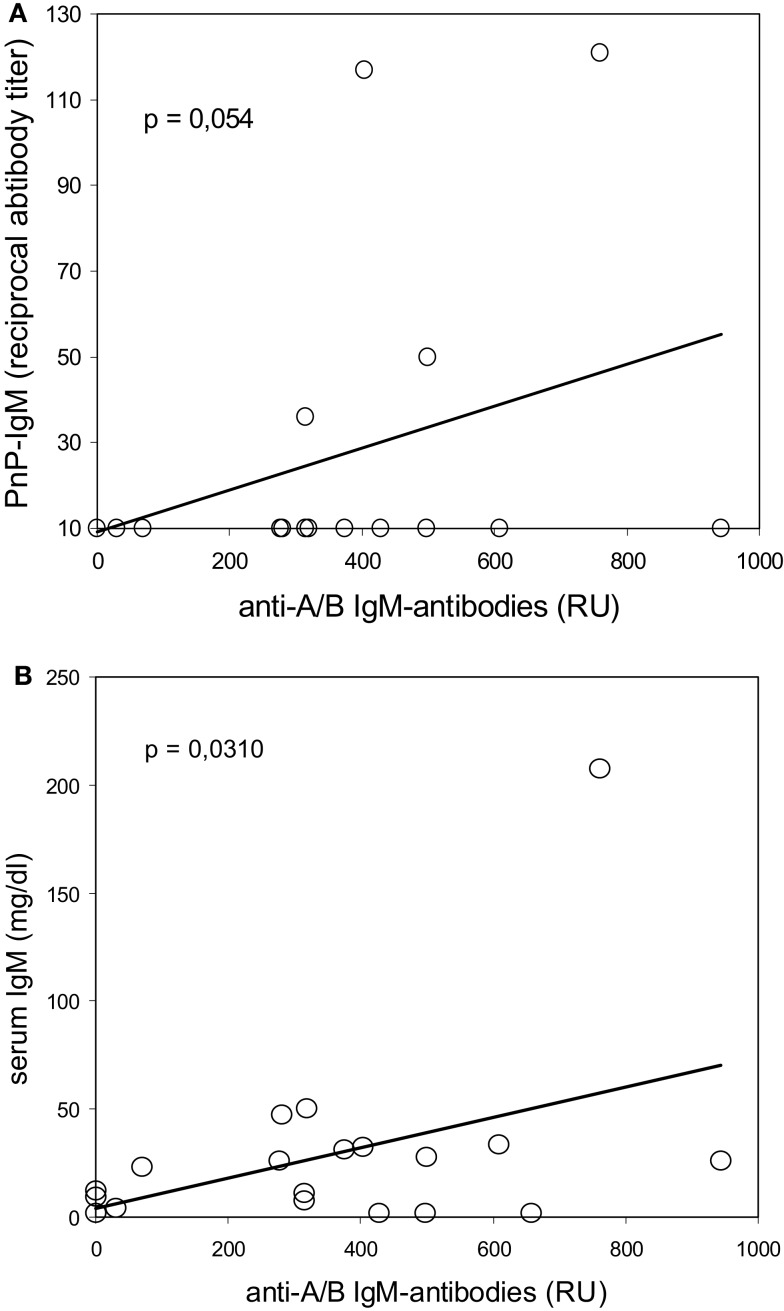
Figure 5.
Correlation between reduced blood group anti-A/B IgM antibodies and defective IgM-antibody response to pneumococcal polysaccharides (upper panel) or reduced serum IgM levels (lower panel) in CVID patients. Serum IgM antibodies against 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharides (PnP–IgM) were determined by ELISA, serum blood group anti-A/B IgM antibodies were assessed using isotype-specific surface plasmon resonance technology, serum IgM levels were measured by nephelometry. Results are depicted as reciprocal serum titer (for PnP–IgM), resonance units (RU, for anti-A/B IgM-antibodies), and mg/dl (for serum IgM). The Bravais–Pearson-correlation coefficient was calculated to determine a statistically significant correlation at a level ofP < 0.05.