Figure 7.
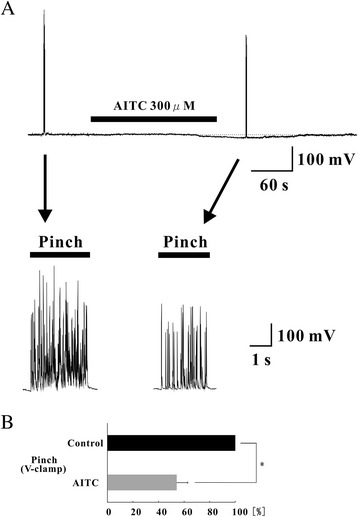
Analysis of the response to pinch stimuli in the presence of AITC under hyperpolarization. (A) Continuous chart recording of membrane potential before and during the action of AITC (300 μM; top). Pinch stimuli applied to the ipsilateral hindlimb produced a barrage of EPSPs accompanied by action potentials under a current-clamp condition (bottom left). AITC (300 μM) hyperpolarized the membrane of a SG neuron and inhibited the action potentials (bottom right). (B) Analysis of evoked EPSPs and action potentials with noxious stimuli to the ipsilateral hindlimb. The area significantly decreased during AITC perfusion compared with control in the absence of AITC (n = 5). *P < 0.05.
