Figure 3.
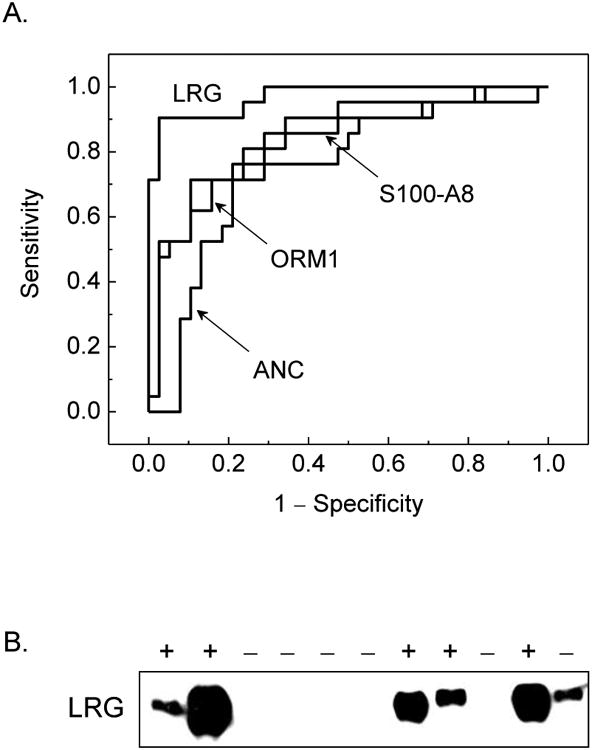
A. Receiver operating characteristics of urine protein markers validated by targeted mass spectrometry, demonstrating the relative diagnostic performance of leucine-rich α-2-glycoprotein (LRG), calgranulin A (S100-A8), α-1-acid glycoprotein 1 (ORM1), and peripheral blood absolute neutrophil count (ANC). The listed confidence intervals were computed for single comparisons, and do not include possible correction for multiple testing, which is expected to broaden them in proportion to the correlation and number of simultaneous tests. B. Enrichment of LRG in a random sample of urine of patients with histologically proven appendicitis (+) as compared to those without (−) by using Western immunoblotting. LRG signal was observed in 5/5 patients with appendicitis and no signal was observed in 5/6 patients without appendicitis. Development of quantitative LRG urine immunoblotting and assessment of its diagnostic performance in interventional studies are important directions of future work.
