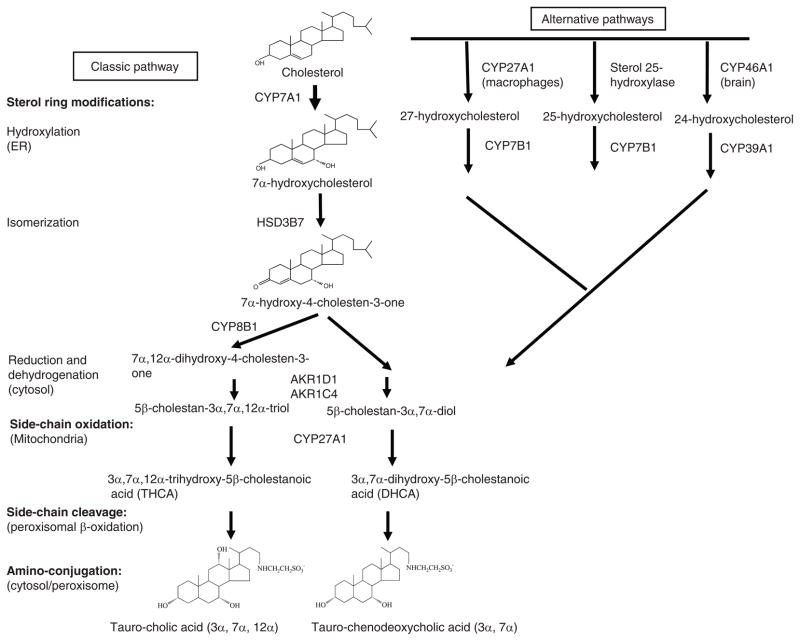
Figure 1.
Bile acid biosynthetic pathways. Two major bile acid biosynthetic pathways are shown. The neutral (or classic) pathway is initiated by cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) located in the endoplasmic reticulum of the liver, whereas the acidic (or alternative) pathway is initiated by mitochondrial sterol 27-hydroxylase (CYP27A1). There are three sterol hydroxylases that convert cholesterol to oxysterols: CYP27A1 in macrophages and other tissues, microsomal sterol 25-hydroxylase in liver microsomes, and sterol 24-hydroxylase (CYP46A1) in the brain. Oxysterol 7α-hydroxylase (CYP7B1) is nonspecific and catalyzes hydroxylation of 27- and 25-hydroxycholesterol to 3β, 7α-dihydroxy-5-cholestenoic acid and 5-cholesten-3β, 7α, 25-triol, respectively. A brain-specific oxysterol 7α-hydroxylase (CYP39A1) catalyzes hydroxylation of 24-hydroxycholesterol to 5-cholesten-3β, 7α, 24(S)-triol. These oxysterols could be converted to CDCA if transported to the liver. In the liver, 3β-hydoxysteroid dehydrogenase (3βHSD, HSD3B7) convert 7α-hydroxycholesterol to 7α-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one (C4), which is converted to 7α, 12α-dihydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one by a sterol 12α-hydroxylase (CYP8B1), leading to synthesis of cholic acid (CA). Without 12α-hydroxylation, the pathway produces CDCA. Aldos-keto reductase 1D1 (AKR1D1) and AKR1C1 catalyze isomerization and saturation of the steroid ring. Then CYP27A1 catalyzes steroid side-chain oxidation to form cholestanoic acids, THCA, and DHCA. Bile acid-Co-A synthase (BACS) or very long-chain Co-A synthase (VLCS) in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) ligates Co-A to the carboxyl groups. Bile acid thioesters are transported into peroxisomes, where an α-methylacyl-CoA racemase (AMACR) converts the methyl group from 25(R) to 25(S) conformation, and three peroxisomal β-oxidation enzymes, branched-chain acyl-CoA oxidase, D-bifunctional enzyme, and thiolase (or sterol carrier protein x) catalyze oxidative cleavage of a propionyl group from the steroid side-chain to form cholyl-CoA and chenodeoxycholyl-CoA. Cytosolic or peroxisomal bile acid: amino-acid transferase (BAAT) catalyzes conjugation of amino acids, glycine or taurine to the carboxyl group of cholyl-CoA and chenodeoxycholyl-CoA to form tauro- or glycol-conjugated CA or CDCA. ER: endoplasmic reticulum.