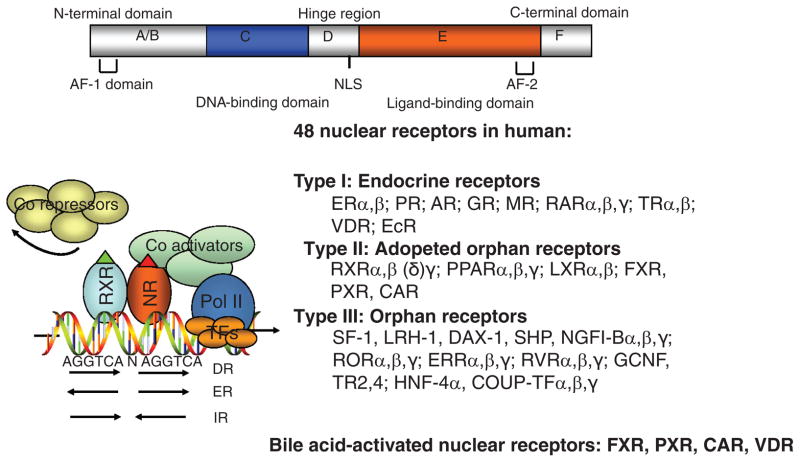
Figure 4.
Nuclear receptors. The general structure of nuclear receptors is shown on the top. The NR1 family of genes involved in metabolic regulation, and their respective endogenous ligands are shown. The putative nuclear receptor response element binding sequence, arranged in direct repeat (DR), everted repeat (ER), and inverted repeat (IR), is shown. Ligand-activated receptors recruit coactivators to replace corepressors and results in transactivation of target gene expression. AF-1-2, activation function-1 and -2; CAR, constitutive androstane receptor; FXR, farnesoid X receptor; LXR, liver orphan receptor; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; PXR, pregnane X receptor; NLS, nuclear localization sequence.