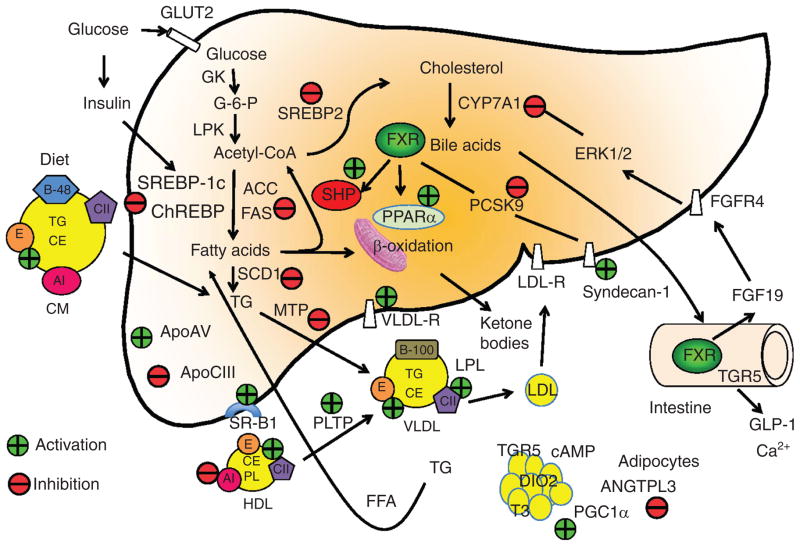
Figure 8.
Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) regulation of hepatic glucose and lipid metabolism in liver, adipocytes, and intestine. Glucose and insulin stimulate glycolysis to form acetyl-CoA, which is a precursor of cholesterol and fatty acids. The FXR/small heterodimer partner (SHP) pathway may inhibit steroid response element binding protein 1c (SREBP-1c), which induces all genes involved in lipogenesis, acetyl CoA carboxylase (ACC), fatty acid synthase (FAS), and stearoyl CoA desaturase (SCD). The FXR/SHP pathway also inhibits SREBP-2, which induces all genes in de novo cholesterol synthesis. FXR activates mitochondria fatty acid β-oxidation by inducing peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα). FXR inhibits PCSK9, which is an inhibitor of LDL receptor. Thus FXR induces LDL-R and also syndecan-1 involved in cholesterol uptake. FXR inhibits mitochondria triglyceride transport protein (MTP), which is required for assembly of VLDL particles with ApoB100. FXR also induces ApoE, which is a high affinity ligand of LDL receptor and scavenger receptor B1 (SR-B1), and a component of VLDL and chylomicron remnants, which are taken up by ApoE receptors. FXR also induces phospholipid transport protein (PLTP) involved in reverse cholesterol transport of cholesterol from peripheral tissues to liver by HDL/SR-B1 receptor-mediated mechanisms. On the other hand, FXR inhibits ApoA1, a component of HDL, and ANGPTL3, which is involved in hydrolysis of triglycerides in liver and adipocytes. FXR induces FGF19 synthesis in the intestine, which activates FGFR4 receptor in hepatocytes to activate ERK1/2 signaling to inhibit CYP7A1 and bile acid synthesis. In colon, bile acids activate TGR5 signaling to stimulate GLP-1 release. GLP-1 increases insulin sensitivity. TGR5 in brown adipocytes stimulates cAMP production, which induce deiodinase 2 (DIO2) to convert T4 to T3, which stimulates mitochondrial energy metabolism via activation of PGC-1α.