Figure 1.
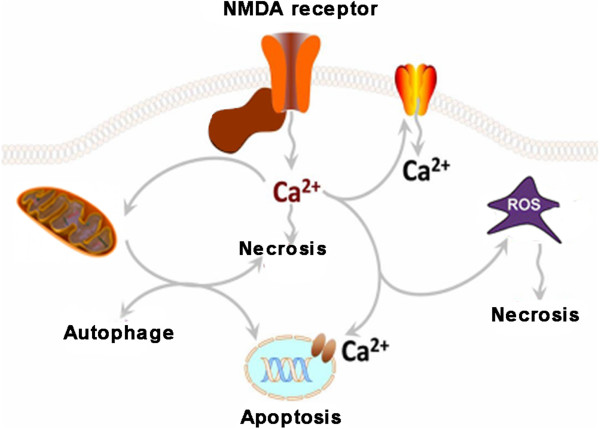
Excitatory neurotransmitter (glutamate) acts at extrasynapses and over-activates NMDA receptors in stroke. Over-activation of NMDA receptor leads to excessive Ca2+ loading into cells. Overloading of Ca2+ induce mitochondria injury, thus causes necrosis and generation of ROS/RNS. On the other hand, excessive intracellular Ca2+ also activate Ca2+ channels on nuclear membrane, causing DNA damage and cell apoptosis. DNA damage also promotes the expression of apoptosis and autophagy related genes, and finally induce cell apoptosis and autophagy.
