Figure 1.
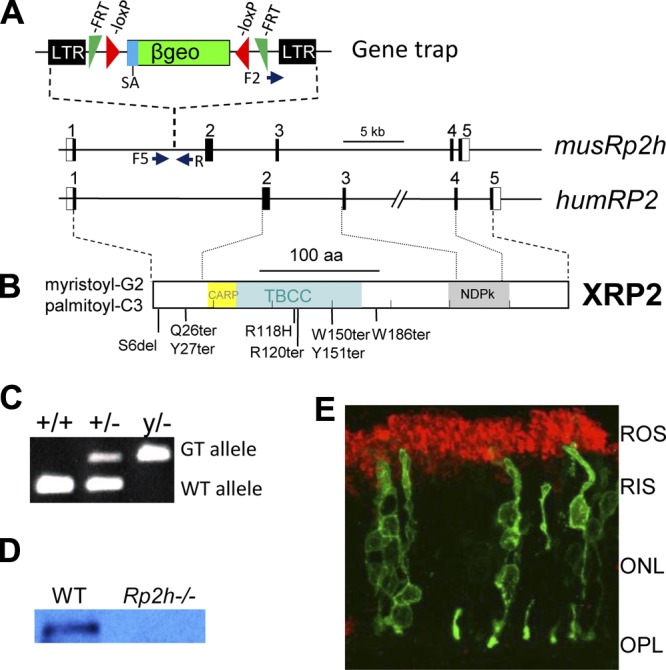
The mouse Rp2h gene knockout. A) The mouse Rp2h gene contains 5 exons. A gene trap located in intron 1 of mouse Rp2h truncates RP2 after lysine 32 (K31). The trap contains long terminal repeats (LTR), a splice acceptor (SA), a β-Geo selective cassette containing β-gal and neo genes. A pair of FRT and loxP recombination signals in antisense orientation flanks the β-Geo cassette. RP2-F1, RP2-F5, and RP2-R are the primers used for genotyping. Underneath, the human RP2 gene; positions of some of the most common RP-associated mutations are shown. B) The human RP2 polypeptide that is myristoylated and palmitoylated at the N-terminal. CARP, cyclase-associated domain; TBBC, tubulin binding cofactor C domain; NDP, nucleoside diphosphate kinase domain. C) Genotyping. The WT allele was genotyped using the primers of RP2-F1 and RP2-R. The mutant Rp2h allele carrying the gene trap was genotyped using the primers of RP2-F5 and RP2-R. D) Immunoblot of WT and knockout retina lysates using an anti-RP2 antibody. E) Localization of RP2-eGFP in WT mouse photoreceptors. Mouse photoreceptors expressing RP2-eGFP (green) were colabeled with rhodopsin (red). ROS, rod outer segment; RIS, rod inner segment; ONL, outer nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer.
