Fig. 4.
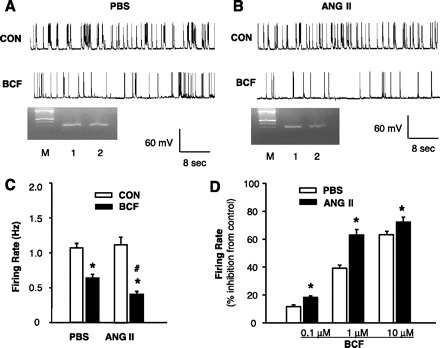
Effect of ANG II on the neuronal responsiveness to GBR agonist baclofen in neuronal cultures. A: representative tracing showing neuronal spontaneous action potentials (APs) recorded from a PBS-treated neuron under basal conditions (CON) and during superfusion of baclofen (BCF, 1 μM). APs were recorded from an AT1R-positive neuron identified by single-cell RT-PCR. B: representative tracing showing APs recorded from an ANG II-treated neuron under basal conditions (CON) and during superfusion of baclofen. APs were recorded from an AT1R-positive neuron by the same methods as in A. Ethidium bromide-stained gels seen in A and B show the PCR DNA products that correspond to AT1R mRNA obtained from the same neuron after the electrophysiological recordings (lanes 2). The RNA from the whole dishes of neurons was used as positive control (lanes 1). M, marker. C: effect of baclofen (1 μM) on neuronal firing in AT1R-positive neurons pretreated with ANG II or PBS control. Data are means ± SE (n = 7). D: dose-dependent inhibition induced by baclofen on neuronal firing in AT1R-positive neurons pretreated with ANG II or PBS control. *P < 0.05 compared with respective control recording; #P < 0.05 compared with PBS treatment.
